VIP activates primordial follicles of rat through ERK-mTOR pathway in tissue culture
- PMID: 30817320
- PMCID: PMC6433003
- DOI: 10.1530/REP-18-0466
VIP activates primordial follicles of rat through ERK-mTOR pathway in tissue culture
Abstract
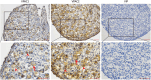
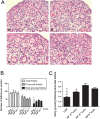
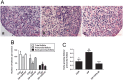
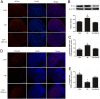
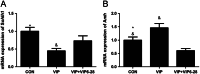
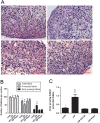
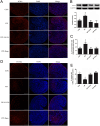
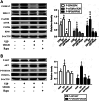
In vitro activation of primordial follicles is becoming more essential in assisted reproductive technologies. Vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP) is one of the members of the neurotrophin family which has demonstrated to have an impact on follicle development in recent years. This study aims to investigate the effect of VIP on the activation of primordial follicles in neonatal rat in an in vitro culture system and to determine the relevant molecular mechanism of their activation. Ovaries of 4-day-old rats were examined for the expression of VIP receptors and were cultured in mediums containing VIP with or without inhibitors of the ERK-mTOR signalling pathway. They were then collected for histological analysis or measurement of the molecular expression of this pathway. The receptors of VIP were found in granular cells and oocytes of primordial and early-growing follicles in neonatal ovary. The ratio of growing follicle increased in the presence VIP at different concentrations, with the highest level of increase being observed in the 10-7 mol/L VIP-treated group. The ratio of PCNA-positive granular cells was also increased, while that of the apoptotic oocytes were decreased, and protein analysis showed increased phosphorylation of ERK1/2, mTOR and RPS6 in the VIP-treated group. However, the effect of VIP on the activation of primordial follicle became insignificant with the addition of MEK inhibitor (U0126) or mTORC1 inhibitor (rapamycin). This study indicated that VIP could activate neonatal rat primordial follicle through the ERK-mTOR signalling pathway, suggesting a strategy for in vitro primordial follicle recruitment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Figures
References
-
- Barberi M, Muciaccia B, Morelli MB, Stefanini M, Cecconi S, Canipari R. 2007. Expression localization and functional activity of pituitary adenylate cyclase-activating polypeptide, vasoactive intestinal polypeptide and their receptors in mouse ovary. Reproduction 134 281–292. ( 10.1530/REP-07-0051) - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bruno JB, Celestino JJ, Lima-Verde IB, Matos MH, Lima LF, Name KP, Araújo VR, Saraiva MV, Martins FS, Campello CC. et al. 2010. Vasoactive intestinal peptide improves the survival and development of caprine preantral follicles after in vitro tissue culture. Cells Tissues Organs 191 414–421. ( 10.1159/000272317) - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

