Takotsubo cardiomyopathy and giant r wave syndrome mimicking acute myocardial infarction: A case report
- PMID: 30817596
- PMCID: PMC6831224
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000014677
Takotsubo cardiomyopathy and giant r wave syndrome mimicking acute myocardial infarction: A case report
Abstract
Rationale: The clinical features of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy largely overlap with those of acute myocardial infarction, especially in the presence of ST-segment elevation on the initial electrocardiogram. Giant R wave syndrome has mainly been observed in the hyperacute phase of acute myocardial infarction.
Patient concerns: In this study, we report a unique case of Takotsubo cardiomyopathy that caused giant R wave syndrome.
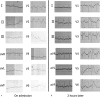
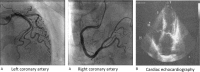
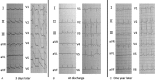
Diagnosis: A 71-year-old woman was transferred to hospital with new onset chest pain. An initial electrocardiogram showed ST-segment elevation in the inferior wall and anterior wall leads. Her initial cardiac troponin I levels were elevated. Acute myocardial infarction was suspected and the patient underwent emergent cardiac catheterization. A coronary angiography showed no overt stenosis in the coronary artery. After 2 hours, her chest pain disappeared and an electrocardiogram revealed that the ST segment had decreased markedly. However, on day 3, an electrocardiogram of the V1-V6 leads revealed the formation of giant R wave syndrome: giant R waves merging with the markedly elevated ST segments and the obliteration of S waves. Cardiac echocardiography showed hypokinetic apical mid-segments and hyperkinetic basal segments of the left ventricle, low left ventricular ejection (42%), and enlargement of the left ventricle. On the basis of these findings, the patient was diagnosed with early recurrent Takotsubo cardiomyopathy.
Interventions: The patient has been treated by levosimendan and furosemide to improve cardiac function before leaving the hospital. After discharge, she was treated with a beta blocker.
Outcomes: The patient was discharged 2 weeks later in stable condition without chest pain. One year later, during her follow-up, a repeat echocardiogram and ECG showed normal findings.
Lessons: To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of giant R wave syndrome on electrocardiogram following Takotsubo cardiomyopathy. Takotsubo cardiomyopathy, especially presenting with giant R wave syndrome on electrocardiogram, remains a challenging condition given its similarity to acute myocardial infarction in its early phase.
Figures
References
-
- Templin C, Ghadri JR, Diekmann J, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of Takotsubo (stress) cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 2015;373:929–38. - PubMed
-
- Akashi YJ, Nef HM, Mollmann H, et al. Stress cardiomyopathy. Ann Rev Med 2010;61:271–86. - PubMed
-
- Prasad A, Lerman A, Rihal CS. Apical ballooning syndrome (Tako-Tsubo or stress cardiomyopathy): a mimic of acute myocardial infarction. Am Heart J 2008;155:408–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

