A single nucleotide polymorphism in dopamine beta hydroxylase (rs6271(C>T)) is over-represented in inflammatory bowel disease patients and reduces circulating enzyme
- PMID: 30817802
- PMCID: PMC6394932
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0210175
A single nucleotide polymorphism in dopamine beta hydroxylase (rs6271(C>T)) is over-represented in inflammatory bowel disease patients and reduces circulating enzyme
Abstract
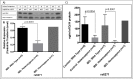
Inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD) are associated with altered neuronal regulation of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract and release of norepinephrine (NE). As sympathetic innervation of the GI tract modulates motility, blood flow, and immune function, changes in NE signaling may alter the risk of developing IBD. Dopamine beta-hydroxylase (DβH), the enzyme responsible for NE production, has been suggested to play a critical role in IBD, however the exact mechanism is unknown. We hypothesized that genetic variants of DβH could increase the risk of IBD. We performed genetic analysis on 45 IBD patients and 74 controls. IBD patients were screened by targeted exome sequencing and compared with NeuroX DβH single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) genotyping data of the controls. Serum DβH protein levels for 15 IBD patients and 13 controls were evaluated using immunoblots and competitive ELISA. Seven SNPs were observed from DβH targeted exome sequencing in the 45 IBD patients. A single non-synonymous SNP, rs6271 (Arg549Cys), had a significant association with IBD patients; the odds ratio was a 5.6 times higher SNP frequency in IBD patients compared to controls (p = 0.002). We also examined the function and availability of the protein in both the IBD and control patients' sera bearing DβH Arg549Cys. Both control and IBD subjects bearing the heterozygote allele had statistically lower DβH protein levels while the intrinsic enzyme activity was higher. This is the first report of a noradrenergic genetic polymorphism (rs6271; Arg549Cys) associated with IBD. This polymorphism is associated with significantly lower levels of circulating DβH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Genotype-controlled analysis of plasma dopamine beta-hydroxylase activity in psychotic unipolar major depression.Biol Psychiatry. 2002 Mar 1;51(5):358-64. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(01)01349-x. Biol Psychiatry. 2002. PMID: 11904129
-
A genotype-controlled analysis of plasma dopamine beta-hydroxylase in healthy and alcoholic subjects: evidence for alcohol-related differences in noradrenergic function.Biol Psychiatry. 2002 Dec 15;52(12):1151-8. doi: 10.1016/s0006-3223(02)01427-0. Biol Psychiatry. 2002. PMID: 12488060
-
Dopamine beta-hydroxylase and its genetic variants in human health and disease.J Neurochem. 2020 Jan;152(2):157-181. doi: 10.1111/jnc.14893. Epub 2019 Oct 31. J Neurochem. 2020. PMID: 31613389 Review.
-
Human genetics of plasma dopamine beta-hydroxylase activity: applications to research in psychiatry and neurology.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2004 Aug;174(4):463-76. doi: 10.1007/s00213-004-1840-8. Epub 2004 Apr 16. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2004. PMID: 15088079 Review.
-
Linkage analysis of plasma dopamine β-hydroxylase activity in families of patients with schizophrenia.Hum Genet. 2011 Nov;130(5):635-43. doi: 10.1007/s00439-011-0989-6. Epub 2011 Apr 21. Hum Genet. 2011. PMID: 21509519 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
How does dopamine convert into norepinephrine? Insights on the key step of the reaction.J Mol Model. 2025 Jan 3;31(1):32. doi: 10.1007/s00894-024-06256-w. J Mol Model. 2025. PMID: 39751655
-
Reduced Plasma Dopamine-β-Hydroxylase Activity Is Associated With the Severity of Bipolar Disorder: A Pilot Study.Front Psychiatry. 2021 Apr 28;12:566091. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2021.566091. eCollection 2021. Front Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33995135 Free PMC article.
-
Multifactor Dimensionality Reduction Analysis to Evaluate the Association of Dopamine Beta-Hydroxylase (DΒH) Polymorphisms with Susceptibility to Dementia (SADEM Study).Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Aug;60(8):4731-4737. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03367-y. Epub 2023 May 6. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37148523
-
Gastrointestinal Dopamine in Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: A Systematic Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 29;22(23):12932. doi: 10.3390/ijms222312932. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34884737 Free PMC article.
-
Risk and Resilience Variants in the Retinoic Acid Metabolic and Developmental Pathways Associated with Risk of FASD Outcomes.Biomolecules. 2024 May 10;14(5):569. doi: 10.3390/biom14050569. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38785976 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collins SM. The immunomodulation of enteric neuromuscular function: implications for motility and inflammatory disorders. Gastroenterology. 1996;111(6):1683–99. Epub 1996/12/01. . - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

