Insight Into Molecular Determinants of T3 vs T4 Recognition From Mutations in Thyroid Hormone Receptor α and β
- PMID: 30817817
- PMCID: PMC6599431
- DOI: 10.1210/jc.2018-02794
Insight Into Molecular Determinants of T3 vs T4 Recognition From Mutations in Thyroid Hormone Receptor α and β
Abstract
Context: The two major forms of circulating thyroid hormones (THs) are T3 and T4. T3 is regarded as the biologically active hormone because it binds to TH receptors (TRs) with greater affinity than T4. However, it is currently unclear what structural mechanisms underlie this difference in affinity.
Objective: Prompted by the identification of a novel M256T mutation in a resistance to TH (RTH)α patient, we investigated Met256 in TRα1 and the corresponding residue (Met310) in TRβ1, residues previously predicted by crystallographic studies in discrimination of T3 vs T4.
Methods: Clinical characterization of the RTHα patient and molecular studies (in silico protein modeling, radioligand binding, transactivation, and receptor-cofactor studies) were performed.
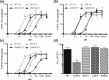
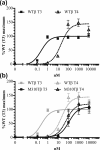
Results: Structural modeling of the TRα1-M256T mutant showed that distortion of the hydrophobic niche to accommodate the outer ring of ligand was more pronounced for T3 than T4, suggesting that this substitution has little impact on the affinity for T4. In agreement with the model, TRα1-M256T selectively reduced the affinity for T3. Also, unlike other naturally occurring TRα mutations, TRα1-M256T had a differential impact on T3- vs T4-dependent transcriptional activation. TRα1-M256A and TRβ1-M310T mutants exhibited similar discordance for T3 vs T4.
Conclusions: Met256-TRα1/Met310-TRβ1 strongly potentiates the affinity of TRs for T3, thereby largely determining that T3 is the bioactive hormone rather than T4. These observations provide insight into the molecular basis for underlying the different affinity of TRs for T3 vs T4, delineating a fundamental principle of TH signaling.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Contrasting Phenotypes in Resistance to Thyroid Hormone Alpha Correlate with Divergent Properties of Thyroid Hormone Receptor α1 Mutant Proteins.Thyroid. 2017 Jul;27(7):973-982. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0157. Thyroid. 2017. PMID: 28471274 Free PMC article.
-
Two Novel Cases of Resistance to Thyroid Hormone Due to THRA Mutation.Thyroid. 2020 Aug;30(8):1217-1221. doi: 10.1089/thy.2019.0602. Epub 2020 Apr 23. Thyroid. 2020. PMID: 32204686
-
The In Vitro Functional Impairment of Thyroid Hormone Receptor Alpha 1 Isoform Mutants Is Mainly Dictated by Reduced Ligand Sensitivity.Thyroid. 2019 Dec;29(12):1834-1842. doi: 10.1089/thy.2019.0019. Epub 2019 Nov 19. Thyroid. 2019. PMID: 31530256
-
Thyroid hormone resistance: Mechanisms and therapeutic development.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2022 Aug 1;553:111679. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2022.111679. Epub 2022 Jun 20. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35738449 Review.
-
Syndromes of Resistance to Thyroid Hormone Action.Exp Suppl. 2019;111:55-84. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-25905-1_5. Exp Suppl. 2019. PMID: 31588528 Review.
Cited by
-
Intein-mediated thyroid hormone biosensors: towards controlled delivery of hormone therapy.Front Syst Biol. 2024 Apr 3;4:1270071. doi: 10.3389/fsysb.2024.1270071. eCollection 2024. Front Syst Biol. 2024. PMID: 40809142 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical and Biochemical Characteristics of Untreated Adult Patients With Resistance to Thyroid Hormone Alpha.J Endocr Soc. 2023 Jul 4;7(8):bvad089. doi: 10.1210/jendso/bvad089. eCollection 2023 Jul 3. J Endocr Soc. 2023. PMID: 37469961 Free PMC article.
-
MAFLD in Patients with Cushing's Disease Is Negatively Associated with Low Free Thyroxine Levels Rather than with Cortisol or TSH Levels.Int J Endocrinol. 2023 Apr 12;2023:6637396. doi: 10.1155/2023/6637396. eCollection 2023. Int J Endocrinol. 2023. PMID: 37091746 Free PMC article.
-
Thyroid Hormone Abuse in Elite Sports: The Regulatory Challenge.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Aug 18;107(9):e3562-e3573. doi: 10.1210/clinem/dgac223. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022. PMID: 35438767 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-invasive Assay for Measurement of Fecal Triiodothyronine (T3) Metabolite Levels in European Mouflon (Ovis aries musimon).Front Vet Sci. 2022 May 30;9:851794. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.851794. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35711806 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gross J, Pitt-Rivers R. Physiological activity of 3:5:3′-L-triiodothyronine. Lancet. 1952;1(6708):593–594. - PubMed
-
- Pitt-Rivers R. Metabolic effects of compounds structurally related to thyroxine in vivo: thyroxine derivatives. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1954;14(11):1444–1450. - PubMed
-
- Mussett MV, Pitt-Rivers R. The thyroid-like activity of triiodothyronine analogues. Lancet. 1954;267(6850):1212–1213. - PubMed
-
- Lerman J. The contribution of triiodothyronine to thyroid physiology. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1954;14(6):690–693. - PubMed

