SLC35A2-CDG: Functional characterization, expanded molecular, clinical, and biochemical phenotypes of 30 unreported Individuals
- PMID: 30817854
- PMCID: PMC6661012
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.23731
SLC35A2-CDG: Functional characterization, expanded molecular, clinical, and biochemical phenotypes of 30 unreported Individuals
Abstract
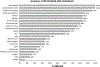
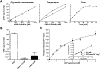
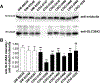
Pathogenic de novo variants in the X-linked gene SLC35A2 encoding the major Golgi-localized UDP-galactose transporter required for proper protein and lipid glycosylation cause a rare type of congenital disorder of glycosylation known as SLC35A2-congenital disorders of glycosylation (CDG; formerly CDG-IIm). To date, 29 unique de novo variants from 32 unrelated individuals have been described in the literature. The majority of affected individuals are primarily characterized by varying degrees of neurological impairments with or without skeletal abnormalities. Surprisingly, most affected individuals do not show abnormalities in serum transferrin N-glycosylation, a common biomarker for most types of CDG. Here we present data characterizing 30 individuals and add 26 new variants, the single largest study involving SLC35A2-CDG. The great majority of these individuals had normal transferrin glycosylation. In addition, expanding the molecular and clinical spectrum of this rare disorder, we developed a robust and reliable biochemical assay to assess SLC35A2-dependent UDP-galactose transport activity in primary fibroblasts. Finally, we show that transport activity is directly correlated to the ratio of wild-type to mutant alleles in fibroblasts from affected individuals.
Keywords: UDP-galactose; congenital disorders of glycosylation; glycoside; nucleotide sugar transporter.
© 2019 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The Department of Molecular and Human Genetics at Baylor College of Medicine derives revenue from clinical genetic testing completed at Baylor Genetics Laboratories. Fernando Scaglia is involved in clinical trials supported by BioElectron, Reata Pharmaceuticals, and Stealth BioTherapeutics. Mary Willis declares views expressed herein are those of the authors and do not necessarily reflect the official policy or position of the Department of the Navy, Department of Defense, or the U.S. Government. Zöe Powis, Jesse M. Hunter, Sha Tang are employed by Ambry Genetics. Sharon F. Suchy, Jane Juusola, Dianalee McKnight, Maria Guillen Sacato and Hui Yang are employed by GeneDx, Inc., a wholly-owned subsidiary of OPKO Health, Inc. The other authors have no conflict.
Figures

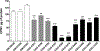

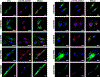
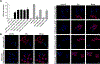
References
-
- Brandli AW, Hansson GC, Rodriguez-Boulan E, & Simons K (1988). A polarized epithelial cell mutant deficient in translocation of UDP-galactose into the Golgi complex. J Biol Chem, 263(31), 16283–16290. - PubMed
-
- Brockhausen I, & Stanley P (2015). O-GalNAc Glycans In rd, Varki A, Cummings RD, Esko JD, Stanley P, Hart GW, Aebi M, Darvill AG, Kinoshita T, Packer NH, Prestegard JH, Schnaar RL, & Seeberger PH (Eds.), Essentials of Glycobiology (pp. 113–123). Cold Spring; Harbor (NY).
-
- Bruneel A, Cholet S, Drouin-Garraud V, Jacquemont ML, Cano A, Megarbane A, … Fenaille F (2018). Complementarity of electrophoretic, mass spectrometric, and gene sequencing techniques for the diagnosis and characterization of congenital disorders of glycosylation. Electrophoresis. doi: 10.1002/elps.201800021 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- T32 GM008638/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007690/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD090257/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007674/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007672/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 NS092898/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007943/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS050375/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007708/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 TR001395/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007709/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 NS093793/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007530/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK099551/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007703/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS058721/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG007942/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

