A rat model of organophosphate-induced status epilepticus and the beneficial effects of EP2 receptor inhibition
- PMID: 30818067
- PMCID: PMC6708729
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2019.02.010
A rat model of organophosphate-induced status epilepticus and the beneficial effects of EP2 receptor inhibition
Abstract
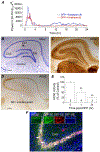
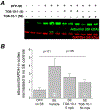
This review describes an adult rat model of status epilepticus (SE) induced by diisopropyl fluorophosphate (DFP), and the beneficial outcomes of transient inhibition of the prostaglandin-E2 receptor EP2 with a small molecule antagonist, delayed by 2-4 h after SE onset. Administration of six doses of the selective EP2 antagonist TG6-10-1 over a 2-3 day period accelerates functional recovery, attenuates hippocampal neurodegeneration, neuroinflammation, gliosis and blood-brain barrier leakage, and prevents long-term cognitive deficits without blocking SE itself or altering acute seizure characteristics. This work has provided important information regarding organophosphate-induced seizure related pathologies in adults and revealed the effectiveness of delayed EP2 inhibition to combat these pathologies.
Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase; Albumin; Cyclooxygenase-2; Diisopropyl fluorophosphate; EP2; Neurodegeneration; Neuroinflammation; Organophosphorus; Status epilepticus.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURE STATEMENT:
There are no conflicts of interest in relation to this work. We confirm that we have read the Journal's position on issues involved in ethical publication and affirm that this manuscript is consistent with the Journal's guidelines.
Figures



References
-
- Apland JP, Aroniadou-Anderjaska V, Figueiredo TH, Rossetti F, Miller SL, & Braga MF (2014). The limitations of diazepam as a treatment for nerve agent-induced seizures and neuropathology in rats: comparison with UBP302. J Pharmacol Exp Ther, 351(2), 359–372. doi:10.1124/jpet.114.217299 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bankstahl M, Breuer H, Leiter I, Markel M, Bascunana P, Michalski D, Bengel FM, Loscher W, Meier M, Bankstahl JP, & Hartig W (2018). Blood-Brain Barrier Leakage during Early Epileptogenesis Is Associated with Rapid Remodeling of the Neurovascular Unit. eNeuro, 5(3). doi:10.1523/ENEURO.0123-18.2018 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

