Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Exposure Promotes Oxidative Stress and Suppresses Sp1 Transcription Factor in Cancer Stem Cells
- PMID: 30818757
- PMCID: PMC6429440
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20051027
Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Exposure Promotes Oxidative Stress and Suppresses Sp1 Transcription Factor in Cancer Stem Cells
Abstract
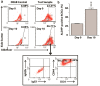
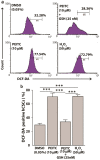
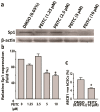
Aldehyde dehydrogenase 1 (ALDH1) is a cytosolic marker of cancer stem cells (CSCs), which are a sub-population within heterogeneous tumor cells. CSCs associate with therapy-resistance, self-renewal, malignancy, tumor-relapse, and reduced patient-survival window. ALDH1-mediated aldehyde scavenging helps CSCs to survive a higher level of oxidative stress than regular cancer cells. Cruciferous vegetable-derived phenethyl isothiocyanate (PEITC) selectively induces reactive oxygen species (ROS), leading to apoptosis of cancer cells, but not healthy cells. However, this pro-oxidant role of PEITC in CSCs is poorly understood and is investigated here. In a HeLa CSCs model (hCSCs), the sphere-culture and tumorsphere assay showed significantly enriched ALDHhi CSCs from HeLa parental cells (p < 0.05). Aldefluor assay and cell proliferation assay revealed that PEITC treatments resulted in a reduced number of ALDHhi hCSCs in a concentration-dependent manner (p < 0.05). In the ROS assay, PEITC promoted oxidative stress in hCSCs (p ≤ 0.001). Using immunoblotting and flow cytometry techniques, we reported that PEITC suppressed the cancer-associated transcription factor (Sp1) and a downstream multidrug resistance protein (P-glycoprotein) (both, p < 0.05). Furthermore, PEITC-treatment of hCSCs, prior to xenotransplantation in mice, lowered the in vivo tumor-initiating potential of hCSCs. In summary, PEITC treatment suppressed the proliferation of ALDH1 expressing cancer stem cells as well as key factors that are involved with drug-resistance, while promoting oxidative stress and apoptosis in hCSCs.
Keywords: ALDH1; apoptosis; cancer stem cells; phenethyl isothiocyanate; reactive oxygen species.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phenethyl isothiocyanate upregulates death receptors 4 and 5 and inhibits proliferation in human cancer stem-like cells.BMC Cancer. 2014 Aug 15;14:591. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-591. BMC Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25127663 Free PMC article.
-
Phenethyl isothiocyanate suppresses cancer stem cell properties in vitro and in a xenograft model.Phytomedicine. 2017 Jul 1;30:42-49. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2017.01.015. Epub 2017 Feb 3. Phytomedicine. 2017. PMID: 28545668
-
Phenethyl isothiocyanate inhibits colorectal cancer stem cells by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin pathway.Phytother Res. 2018 Dec;32(12):2447-2455. doi: 10.1002/ptr.6183. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Phytother Res. 2018. PMID: 30159926
-
Phenethyl isothiocyanate: a comprehensive review of anti-cancer mechanisms.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014 Dec;1846(2):405-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2014.08.003. Epub 2014 Aug 23. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2014. PMID: 25152445 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting ROS: selective killing of cancer cells by a cruciferous vegetable derived pro-oxidant compound.Cancer Biol Ther. 2007 May;6(5):646-7. doi: 10.4161/cbt.6.5.4092. Epub 2007 Mar 1. Cancer Biol Ther. 2007. PMID: 17387274 Review.
Cited by
-
Unveiling diagnostic and therapeutic strategies for cervical cancer: biomarker discovery through proteomics approaches and exploring the role of cervical cancer stem cells.Front Oncol. 2024 Jan 24;13:1277772. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1277772. eCollection 2023. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38328436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative stress in cancer: from tumor and microenvironment remodeling to therapeutic frontiers.Mol Cancer. 2025 Aug 22;24(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02375-x. Mol Cancer. 2025. PMID: 40847302 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting Cervical Cancer Stem Cells by Phytochemicals.Curr Med Chem. 2024;31(32):5222-5254. doi: 10.2174/0109298673281823231222065616. Curr Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38288813 Review.
-
Phenethyl Isothiocyanate Suppresses Stemness in the Chemo- and Radio-Resistant Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Cell Line MDA-MB-231/IR Via Downregulation of Metadherin.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Jan 22;12(2):268. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020268. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 31979093 Free PMC article.
-
Targeting the Cancer Stem Cells in Endocrine Cancers with Phytochemicals.Curr Top Med Chem. 2022;22(31):2589-2597. doi: 10.2174/1567205020666221114112814. Curr Top Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36380414
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

