A new age-related cutoff of medial temporal atrophy scale on MRI improving the diagnostic accuracy of neurodegeneration due to Alzheimer's disease in a Chinese population
- PMID: 30819102
- PMCID: PMC6394092
- DOI: 10.1186/s12877-019-1072-8
A new age-related cutoff of medial temporal atrophy scale on MRI improving the diagnostic accuracy of neurodegeneration due to Alzheimer's disease in a Chinese population
Abstract
Background: Visual rating scales are still the most popular tools in assessing atrophy degrees of whole brain and lobes. However, the false negative rate of the previous cutoff score of visual rating scales was relatively high for detecting dementia of Alzheimer's type (DAT). This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic value of new cutoffs of visual rating scales on magnetic resonance imaging for discriminating DAT in a Chinese population.
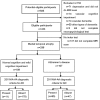
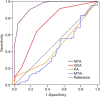
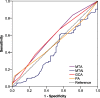
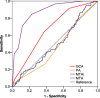
Methods: Out of 585 enrolled subjects, 296 participants were included and diagnosed as normal cognition (NC)(n = 87), 138 diagnosed as amnestic mild cognitive impairment (aMCI), and 71 as dementia of Alzheimer's type (DAT). Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analyses were used to calculate the diagnostic value of visual rating sales (including medial temporal atrophy (MTA), posterior atrophy rating scale (PA),global cortical atrophy scale (GCA) and medial temporal-lobe atrophy index (MTAi))for detecting NC from DAT .
Results: Scores of MTA correlated to age and Mini-mental state examination score. When used to detect DAT from NC, the MTA showed highest diagnostic value than other scales, and when the cutoff score of 1.5 of MTA scale, it obtained an optimal sensitivity (84.5%) and specificity (79.1%) respectively, with a 15.5% of false negative rate. Cutoff scores and diagnostic values were calculated stratified by age. For the age ranges 50-64, 65-74, 75-84 years, the following cut-offs of MTA should be used, ≥1.0(sensitivity and specificity were 92.3 and 68.4%), ≥1.5(sensitivity and specificity were 90.4 and 85.2%), ≥ 2.0(sensitivity and specificity were 70.8 and 82.3%) respectively. All of the scales showed relatively lower diagnostic values for discriminating aMCI from NC.
Conclusions: The new age-based MTA cutoff showed better diagnostic accuracy for detecting DAT than previous standard, the list of practical cut-offs proposed here might be useful in clinical practice.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Global cortical atrophy scale; Medial temporal atrophy scale; Medial temporal-lobe atrophy index; Posterior atrophy rating scale.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The protocol was approved by Dongzhimen Hospital, Beijing University of Chinese Medicine Institutional Ethics Committee. All procedures performed in this study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. All the patients and responsible caregivers provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Practical cut-offs for visual rating scales of medial temporal, frontal and posterior atrophy in Alzheimer's disease and mild cognitive impairment.J Intern Med. 2015 Sep;278(3):277-90. doi: 10.1111/joim.12358. Epub 2015 Apr 13. J Intern Med. 2015. PMID: 25752192
-
Combining Visual Rating Scales for Medial Temporal Lobe Atrophy and Posterior Atrophy to Identify Amnestic Mild Cognitive Impairment from Cognitively Normal Older Adults: Evidence Based on Two Cohorts.J Alzheimers Dis. 2020;77(1):323-337. doi: 10.3233/JAD-200016. J Alzheimers Dis. 2020. PMID: 32716355 Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation and clinical correlation of practical cut-offs for visual rating scales of atrophy: normal aging versus mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer's disease.Acta Neurol Belg. 2017 Sep;117(3):661-669. doi: 10.1007/s13760-017-0777-8. Epub 2017 Apr 10. Acta Neurol Belg. 2017. PMID: 28397182
-
Structural magnetic resonance imaging for the early diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer's disease in people with mild cognitive impairment.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Mar 2;3(3):CD009628. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009628.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 32119112 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical validity of medial temporal atrophy as a biomarker for Alzheimer's disease in the context of a structured 5-phase development framework.Neurobiol Aging. 2017 Apr;52:167-182.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2016.05.024. Neurobiol Aging. 2017. PMID: 28317647 Review.
Cited by
-
Combining visual rating scales to identify prodromal Alzheimer's disease and Alzheimer's disease dementia in a population from a low and middle-income country.Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 1;13:962192. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.962192. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36119675 Free PMC article.
-
CT-based volumetric measures obtained through deep learning: Association with biomarkers of neurodegeneration.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Jan;20(1):629-640. doi: 10.1002/alz.13445. Epub 2023 Sep 28. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 37767905 Free PMC article.
-
Associations of multiple visual rating scales based on structural magnetic resonance imaging with disease severity and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in patients with Alzheimer's disease.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Jul 29;14:906519. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.906519. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35966797 Free PMC article.
-
"Advances in biomarker discovery and diagnostics for alzheimer's disease".Neurol Sci. 2025 Jun;46(6):2419-2436. doi: 10.1007/s10072-025-08023-y. Epub 2025 Feb 1. Neurol Sci. 2025. PMID: 39893357 Review.
-
Comparison of Quantitative Hippocampal Volumes and Structured Scoring Scales in Predicting Alzheimer Disease Diagnosis.AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2023 Dec 11;44(12):1411-1417. doi: 10.3174/ajnr.A8049. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2023. PMID: 38050003 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzheimer’s disease international. World Alzheimer Report 2016. Improving healthcare for people living with dementia. https://www.alz.co.uk/research/WorldAlzheimerReport2016.pdf.
-
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2017 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2017;13(4):325-73. https://www.alz.org/documents_custom/2017-facts-and-figures.pdf.
-
- Li Y, Rinne JO, Mosconi L, Pirraglia E, Rusinek H, DeSanti S, Kemppainen N, Någren K, Kim BC, Tsui W, de Leon MJ. Regional analysis of FDG and PIB-PET images in normal aging, mild cognitive impairment, and Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2008;35:2169–2181. doi: 10.1007/s00259-008-0833-y. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Jack CR, Jr, Shiung MM, Gunter JL, O'Brien PC, Weigand SD, Knopman DS, Boeve BF, Ivnik RJ, Smith GE, Cha RH, Tangalos EG, Petersen RC. Comparison of different MRI brain atrophy rate measures with clinical disease progression in AD. Neurology. 2004;62:591–600. doi: 10.1212/01.WNL.0000110315.26026.EF. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- McKhann GM, Knopman DS, Chertkow H, Hyman BT, Jack CR, Jr, Kawas CH, Klunk WE, Koroshetz WJ, Manly JJ, Mayeux R, Mohs RC, Morris JC, Rossor MN, Scheltens P, Carrillo MC, Thies B, Weintraub S, Phelps CH. The diagnosis of dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations from the National Institute on Aging-Alzheimer’s association workgroups on diagnostic guidelines for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2011;7:263–269. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2011.03.005. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

