Factors Affecting Interindividual Variability of Hepatic UGT2B17 Protein Expression Examined Using a Novel Specific Monoclonal Antibody
- PMID: 30819787
- PMCID: PMC12164694
- DOI: 10.1124/dmd.119.086330
Factors Affecting Interindividual Variability of Hepatic UGT2B17 Protein Expression Examined Using a Novel Specific Monoclonal Antibody
Abstract
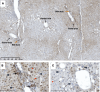
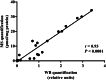
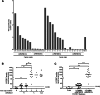
Accurate quantification of the metabolic enzyme uridine diphospho-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT) UGT2B17 has been hampered by the high sequence identity with other UGT2B enzymes (as high as 94%) and by the lack of a specific antibody. Knowing the significance of the UGT2B17 pathway in drug and hormone metabolism and cancer, we developed a specific monoclonal antibody (EL-2B17mAb), initially validated by the lack of detection in liver microsomes of an individual carrying no UGT2B17 gene copy and in supersomes expressing UGT2B enzymes. Immunohistochemical detection in livers revealed strong labeling of bile ducts and variable labeling of hepatocytes. Expression levels assessed by immunoblotting were highly correlated to mass spectrometry-based quantification (r = 0.93), and three major expression patterns (absent, low, or high) were evidenced. Livers with very low expression were carriers of the functional rs59678213 G variant, located in the binding site for the transcription factor forkhead box A1 (FOXA1) of the UGT2B17 promoter. The highest level of expression was observed for individuals carrying at least one rs59678213 A allele. Multiple regression analysis indicated that the number of gene copies explained only 8% of UGT2B17 protein expression, 49% when adding rs59678213, reaching 54% when including sex. The novel EL-2B17mAb antibody allowed specific UGT2B17 quantification and exposed different patterns of hepatic expression. It further suggests that FOXA1 is a key driver of UGT2B17 expression in the liver. The availability of this molecular tool will help characterize the UGT2B17 level in various disease states and establish more precisely the contribution of the UGT2B17 enzyme to drug and hormone metabolism.
Copyright © 2019 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures



References
-
- Beaulieu M, Lévesque E, Hum DW, Bélanger A. Isolation and characterization of a novel cDNA encoding a human UDP-glucuronosyltransferase active on C19 steroids. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:22855–22862. - PubMed
-
- Beaulieu M, Lévesque E, Tchernof A, Beatty BG, Bélanger A, Hum DW. Chromosomal localization, structure, and regulation of the UGT2B17 gene, encoding a C19 steroid metabolizing enzyme. DNA Cell Biol. 1997;16:1143–1154. - PubMed
-
- Bélanger A, Hum DW, Beaulieu M, Lévesque E, Guillemette C, Tchernof A, Bélanger G, Turgeon D, Dubois S. Characterization and regulation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferases in steroid target tissues. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1998;65:301–310. - PubMed
-
- Belledant A, Hovington H, Garcia L, Caron P, Brisson H, Villeneuve L, Simonyan D, Têtu B, Fradet Y, Lacombe L, et al. The UGT2B28 sex-steroid inactivation pathway is a regulator of steroidogenesis and modifies the risk of prostate cancer progression. Eur Urol. 2016;69:601–609. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

