p66Shc deficiency in the Eμ-TCL1 mouse model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia enhances leukemogenesis by altering the chemokine receptor landscape
- PMID: 30819907
- PMCID: PMC6886430
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2018.209981
p66Shc deficiency in the Eμ-TCL1 mouse model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia enhances leukemogenesis by altering the chemokine receptor landscape
Abstract
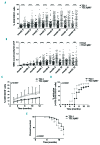
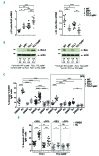
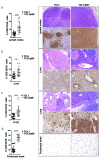
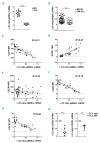
The Shc family adaptor p66Shc acts as a negative regulator of proliferative and survival signals triggered by the B-cell receptor and, by enhancing the production of reactive oxygen species, promotes oxidative stress-dependent apoptosis. Additionally, p66Shc controls the expression and function of chemokine receptors that regulate lymphocyte traffic. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells have a p66Shc expression defect which contributes to their extended survival and correlates with poor prognosis. We analyzed the impact of p66Shc ablation on disease severity and progression in the Eμ-TCL1 mouse model of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. We showed that Eμ-TCL1/p66Shc-/- mice developed an aggressive disease that had an earlier onset, occurred at a higher incidence and led to earlier death compared to that in Eμ-TCL1 mice. Eμ-TCL1/p66Shc-/- mice displayed substantial leukemic cell accumulation in both nodal and extranodal sites. The target organ selectivity correlated with upregulation of chemokine receptors whose ligands are expressed therein. This also applied to chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells, where chemokine receptor expression and extent of organ infiltration were found to correlate inversely with these cells' level of p66Shc expression. p66Shc expression declined with disease progression in Eμ-TCL1 mice and could be restored by treatment with the Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor ibrutinib. Our results highlight p66Shc deficiency as an important factor in the progression and severity of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and underscore p66Shc expression as a relevant therapeutic target.
Copyright© 2019 Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures



Comment in
-
p66Shc deficiency sets the scene for clinically aggressive chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Haematologica. 2019 Oct;104(10):1914-1916. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2019.225904. Haematologica. 2019. PMID: 31575671 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
P66Shc: A Pleiotropic Regulator of B Cell Trafficking and a Gatekeeper in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 19;12(4):1006. doi: 10.3390/cancers12041006. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32325830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel class of oxazepine-based anti-cancer agents induces cell death in primary human CLL cells and efficiently reduces tumor growth in Eμ-TCL1 mice through the JNK/STAT4/p66Shc axis.Pharmacol Res. 2021 Dec;174:105965. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105965. Epub 2021 Oct 31. Pharmacol Res. 2021. PMID: 34732370
-
Impaired expression of p66Shc, a novel regulator of B-cell survival, in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Blood. 2010 May 6;115(18):3726-36. doi: 10.1182/blood-2009-08-239244. Epub 2010 Jan 8. Blood. 2010. PMID: 20061561
-
Par-4 overexpression impedes leukemogenesis in the Eµ-TCL1 leukemia model through downregulation of NF-κB signaling.Blood Adv. 2019 Apr 23;3(8):1255-1266. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018025973. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 30987970 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Selective B Cell Autophagy by the Pro-oxidant Adaptor p66SHC.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020 Mar 26;8:193. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2020.00193. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2020. PMID: 32274384 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
p66Shc Deficiency in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Promotes Chemokine Receptor Expression Through the ROS-Dependent Inhibition of NF-κB.Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 29;12:877495. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.877495. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35847884 Free PMC article.
-
Leukemic cell-secreted interleukin-9 suppresses cytotoxic T cell-mediated killing in chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Feb 15;15(2):144. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06528-6. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38360867 Free PMC article.
-
P66Shc: A Pleiotropic Regulator of B Cell Trafficking and a Gatekeeper in Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Apr 19;12(4):1006. doi: 10.3390/cancers12041006. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32325830 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential New Therapies "ROS-Based" in CLL: An Innovative Paradigm in the Induction of Tumor Cell Apoptosis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2024 Apr 17;13(4):475. doi: 10.3390/antiox13040475. Antioxidants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38671922 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of p66Shc in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Jul;29(14):e70737. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70737. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40690563 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dighiero G, Hamblin TJ. Chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Lancet. 2008;371(9617): 1017–1029. - PubMed
-
- Burger JA. Nurture versus nature: the microenvironment in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Hematol Am Soc Hematol Educ Progr. 2011;2011(1):96–103. - PubMed
-
- Giorgio M, Migliaccio E, Orsini F, et al. Electron transfer between cytochrome c and p66Shc generates reactive oxygen species that trigger mitochondrial apoptosis. Cell. 2005;122(2):221–233. - PubMed
-
- Finetti F, Savino MT, Baldari CT. Positive and negative regulation of antigen receptor signaling by the Shc family of protein adapters. Immunol Rev. 2009;232(1):115–134. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

