Polyphenol-enriched fraction of Vaccinium uliginosum L. protects selenite-induced cataract formation in the lens of Sprague-Dawley rat pups
- PMID: 30820147
- PMCID: PMC6379086
Polyphenol-enriched fraction of Vaccinium uliginosum L. protects selenite-induced cataract formation in the lens of Sprague-Dawley rat pups
Abstract
Purpose: As the aging population is increasing, the incidence of age-related cataract is expected to increase globally. The surgical intervention, a treatment for cataract, still has complications and is limited to developed countries. In this study, we investigated whether the polyphenol-enriched fraction of Vaccinium uliginosum L. (FH) prevents cataract formation in Sprague-Dawley (SD) rat pups.
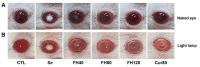
Methods: Sixty rat pups were randomly divided into six groups: CTL, Se, FH40, FH80, FH120, and Cur80. The cataract was induced with subcutaneous injection of sodium selenite (18 μmol/kg bodyweight) on postnatal (P) day 10. All groups, except CTL, were injected with sodium selenite, and the FH40, FH80, and FH120 groups were given gastric intubation with FH40 mg/kg, 80 mg/kg, and 120 mg/kg on P9, P10, and P11. The Cur80 group was also given gastric intubation with curcumin 80 mg/kg on P9, P10, and P11. All rat pups were euthanized on P30.
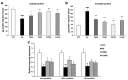
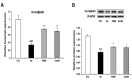
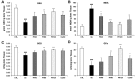
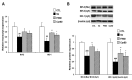
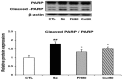
Results: Lens morphological analysis showed that FH dose-dependently inhibited cataract formation. In the Se group, soluble proteins were insolubilized, and the gene expression of the α-, β-, and γ-crystallins was downregulated. However, FH treatment statistically significantly inhibited insolubilization of soluble proteins and downregulation of the gene expression of the α-, β-, and γ-crystallins. In the Se group, the gene and protein levels of m-calpain were downregulated, which were attenuated with FH treatment. In addition, sodium selenite injection caused reduced antioxidant enzymes (superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GPx)), glutathione (GSH) depletion, and malondialdehyde (MDA) production in the lens. The administration of FH inhibited sodium selenite-induced oxidative stress in a dose-dependent manner. The mechanism of protection against oxidative stress by FH involves NF-E2-related factor (Nrf-2) and hemoxygenase-1 (HO-1). FH treatment inhibited decrease of Nrf-2 in the nucleus fraction and HO-1 in the cytosol fraction. Finally, the FH treatment protected poly (ADP)-ribose polymerase (PARP) from cleavage, determined with western blotting.
Conclusions: FH showed a preventive effect against cataract formation by inhibiting m-calpain-mediated proteolysis and oxidative stress in the lens. These results suggest that FH could be a potential anticataract agent in age-related cataract.
Figures
References
-
- Beatty S, Koh H, Phil M, Henson D, Boulton M. The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration. Surv Ophthalmol. 2000;45:115–34. - PubMed
-
- Pascolini D, Mariotti SP. Global estimates of visual impairment: 2010. Br J Ophthalmol. 2012;96:614–8. - PubMed
-
- David LL, Shearer TR. Beta-crystallins insolubilized by calpain II in vitro contain cleavage sites similar to beta-crystallins insolubilized during cataract. FEBS Lett. 1993;324:265–70. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

