Correlation between human neutrophil peptide 1-3 secretion and azurophilic granule (CD63) expression in early childhood caries
- PMID: 30820201
- PMCID: PMC6364345
Correlation between human neutrophil peptide 1-3 secretion and azurophilic granule (CD63) expression in early childhood caries
Abstract
Background: In saliva, neutrophil constitutes the most prominent first-line defense of immune cells against pathogenic microbes. The importance of neutrophils to the host immune systems of neutropenic or patients disabled with regard to their neutrophil function results in a tendency toward serious infections, such as early childhood caries (ECC). The cytoplasmic granules present in neutrophils play a major role in neutrophil-mediated inflammation. Azurophilic granules contain antimicrobial proteins, such as defensin, a human antimicrobial peptide (HNP 1-3). The aim of this study is to analyze the correlation of HNP 1-3 secretion with CD63 expression on the surface of salivary neutrophils.
Materials and methods: This study constituted a cross-sectional, analytical observational study. Saliva taken from preschoolchildren between the ages of 4-6 years who had been divided into two groups, i.e., early childhood caries group with decayed, extracted, filled teeth (def-t) index >6 and caries free with def-t = 0, was subjected to a HNP 1-3 secretion test using ELISA assay and an expression test for CD63 by means of a flow cytometry test. The results obtained were analyzed using independent t-test and Pearson correlation (P < 0.05).
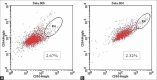
Results: The secretion of HNP 1-3 in the saliva of ECC was higher (172.6 ± 41.64) compared to that of caries-free cases (140.39 ± 31.91), whereas the level of CD63 salivary expression in ECC was lower (2.32 ± 0.57) than in the presence of caries (2.67 ± 0.46).
Conclusion: In ECC cases, saliva increases HNP 1-3 secretion but decreases CD63 expression on the surface of salivary neutrophils.
Keywords: CD63; dental caries; human antimicrobial; neutrophils.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript declare that they have no conflicts of interest, real or perceived, financial or non-financial in this article.
Figures
References
-
- Tanzer JM, Livingston J, Thompson AM. The microbiology of primary dental caries in humans. J Dent Educ. 2001;65:1028–37. - PubMed
-
- Luthfi M, Indrawati R, Arundina I, Dachlan YP. Korelasi Jumlah Streptococcus mutans (S. mutans) dan level ekspresi interlukin 8 (IL-8) pada severe early childhood caries. Maj Ked Gi Ind. 2015;1:142–8.
-
- Nauseef WM, Clark RA. Granulocytic phagocytes. In: Mandell GL, Bennett JE, Dolin R, editors. Mandell, Douglas, and Bennett's Principles and Practice of Infectious Disease. Elsevier/Churchill Livingsone: New York; 2010. pp. 93–117.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous