Real-World Treatment Patterns Among Patients Initiating Small Molecule Kinase Inhibitor Therapies for Thyroid Cancer in the United States
- PMID: 30820872
- PMCID: PMC6824453
- DOI: 10.1007/s12325-019-0890-6
Real-World Treatment Patterns Among Patients Initiating Small Molecule Kinase Inhibitor Therapies for Thyroid Cancer in the United States
Abstract
Introduction: Little is known about real-world use of small molecule kinase inhibitors (SMKI) for advanced thyroid cancer in the United States. This study examined prescribing patterns of SMKI agents recommended by the National Comprehensive Cancer Center (NCCN).
Methods: This retrospective study used a national health insurance database to identify patients diagnosed with thyroid cancer during 1/1/2006-6/30/2016 and with prescription claims for NCCN-recommended SMKI during 1/1/2010-5/31/2016 whose first claim date was the index date. Inclusion also required continuous enrollment in a health plan for 3 months pre-index (baseline) and ≥ 1 month post-index (follow-up) with no claims for SMKI during baseline. Lines of therapy (LOT) were defined by the date of SMKI claims and days of drug supply. Median time to SMKI discontinuation in each LOT was estimated by Kaplan-Meier method.
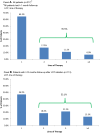
Results: The study included 217 patients. During follow-up (mean duration 499.0 days), 35.5% of patients (n = 77) received a second or later LOT; among patients with ≥ 12 months follow-up after first LOT (LOT1) initiation, 53.1% (n = 60) received a second or later LOT. Median treatment duration was 5.0 months for LOT1 and 5.1 months for LOT2. Over the entire follow-up period (2010-2016), sorafenib was the most common regimen in LOT1 (36.9% of patients) and LOT2 (24.7%) followed by sunitinib and levantinib (13.4% each) in LOT1 and sunitinib (19.5%) in LOT2. Starting in 2015, the year lenvatinib was approved for differentiated thyroid cancer, lenvatinib was the most common first-line regimen among patients initiating LOT1 in 2015 (43.4%) and 2016 (66.7%).
Conclusion: Sorafenib was the most common first-line agent during 2010-2014 but was supplanted by lenvatinib starting in 2015. Approximately 36-53% of patients received a second-line treatment. Median treatment duration results suggested potential benefit of SMKI in second-line therapy. SMKI treatment after first-line failure may be considered for appropriately selected patients.
Funding: Eisai, Inc. (Woodcliff Lake, NJ).
Keywords: Lenvatinib; Sorafenib; Thyroid cancer treatment; Treatment duration.
Figures




References
-
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts & figures 2018. https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-.... Accessed 29 Oct 2018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

