Intestinal NF-κB and STAT signalling is important for uptake and clearance in a Drosophila-Herpetomonas interaction model
- PMID: 30822306
- PMCID: PMC6415867
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1007931
Intestinal NF-κB and STAT signalling is important for uptake and clearance in a Drosophila-Herpetomonas interaction model
Abstract
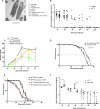
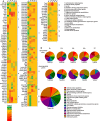
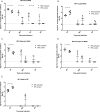
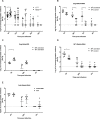
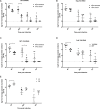
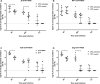
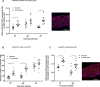
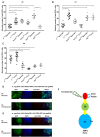
Dipteran insects transmit serious diseases to humans, often in the form of trypanosomatid parasites. To accelerate research in more difficult contexts of dipteran-parasite relationships, we studied the interaction of the model dipteran Drosophila melanogaster and its natural trypanosomatid Herpetomonas muscarum. Parasite infection reduced fecundity but not lifespan in NF-κB/Relish-deficient flies. Gene expression analysis implicated the two NF-κB pathways Toll and Imd as well as STAT signalling. Tissue specific knock-down of key components of these pathways in enterocytes (ECs) and intestinal stem cells (ISCs) influenced initial numbers, infection dynamics and time of clearance. Herpetomonas triggered STAT activation and proliferation of ISCs. Loss of Relish suppressed ISCs, resulting in increased parasite numbers and delayed clearance. Conversely, overexpression of Relish increased ISCs and reduced uptake. Finally, loss of Toll signalling decreased EC numbers and enabled parasite persistence. This network of signalling may represent a general mechanism with which dipteran respond to trypanosomatids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Aksoy S, Lehane M and Levashina E (2004) Immune responses and parasite transmission in blood sucking insects Trends Parasitol 20: 433–439 - PubMed
-
- Lehane MJ, Msangi AR (1991) Lectin and peritrophic membrane development in the gut of Glossina m. morsitans and a discussion of their role in protecting the fly against trypanosome infection Med Vet Entomol 5: 495–501. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

