Water-Dispersible and Biocompatible Iron Carbide Nanoparticles with High Specific Absorption Rate
- PMID: 30822381
- PMCID: PMC7430224
- DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.8b05671
Water-Dispersible and Biocompatible Iron Carbide Nanoparticles with High Specific Absorption Rate
Abstract
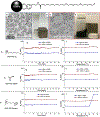
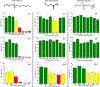
Magnetic nanoparticles are important tools for biomedicine, where they serve as versatile multifunctional instruments for a wide range of applications. Among these applications, magnetic hyperthermia is of special interest for the destruction of tumors and triggering of drug delivery. However, many applications of magnetic nanoparticles require high-quality magnetic nanoparticles displaying high specific absorption rates (SARs), which remains a challenge today. We report here the functionalization and stabilization in aqueous media of highly magnetic 15 nm iron carbide nanoparticles featuring excellent heating power through magnetic induction. The challenge of achieving water solubility and colloidal stability was addressed by designing and using specific dopamine-based ligands. The resulting nanoparticles were completely stable for several months in water, phosphate, phosphate-buffered saline, and serum-containing media. Iron carbide nanoparticles displayed high SARs in water and viscous media (water/glycerol mixtures), even after extended exposition to water and oxygen (SAR up to 1000 W·g-1 in water at 100 kHz, 47 mT). The cytotoxicity and cellular uptake of iron carbide nanoparticles could be easily tuned and were highly dependent on the chemical structure of the ligands used.
Keywords: biocompatibility; functionalization; iron carbide; magnetic hyperthermia; nanoparticles.
Figures


References
-
- Fernandes Cardoso V; Francesko A; Ribeiro C; Banobre-Lopez M; Martins P; Lanceros-Mendez S Advances in Magnetic Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Adv. Healthcare Mater 2018, 7, 1700845. - PubMed
-
- Pankhurst QA; Connolly J; Jones SK; Dobson J Applications of Magnetic Nanoparticles in Biomedicine. J. Phys. D: Appl. Phys 2003, 36, R167–R181.
-
- Lee J-H; Jang J-T; Choi J-S; Moon SH; Noh S-H; Kim J-W; Kim J-G; Kim I-S; Park KI; Cheon J Exchange-Coupled Magnetic Nanoparticles for Efficient Heat Induction. Nat. Nanotech 2011, 6, 418–422. - PubMed
-
- Salunkhe AB; Khot VM; Pawar SH Magnetic Hyperthermia with Magnetic Nanoparticles: a Status Review. Curr. Top. Med. Chem 2014, 14, 572–594. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

