In Vivo Rodent Models of Type 2 Diabetes and Their Usefulness for Evaluating Flavonoid Bioactivity
- PMID: 30823474
- PMCID: PMC6470730
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11030530
In Vivo Rodent Models of Type 2 Diabetes and Their Usefulness for Evaluating Flavonoid Bioactivity
Erratum in
-
Correction: Fang et al. In Vivo Rodent Models of Type 2 Diabetes and Their Usefulness for Evaluating Flavonoid Bioactivity. Nutrients 2019, 11, 530.Nutrients. 2023 Jun 26;15(13):2881. doi: 10.3390/nu15132881. Nutrients. 2023. PMID: 37447402 Free PMC article.
Abstract
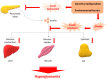
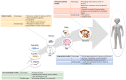
About 40% of the world's population is overweight or obese and exist at risk of developing type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D). Obesity is a leading pathogenic factor for developing insulin resistance (IR). It is well established that IR and a progressive decline in functional β-cell mass are hallmarks of developing T2D. In order to mitigate the global prevalence of T2D, we must carefully select the appropriate animal models to explore the cellular and molecular mechanisms of T2D, and to optimize novel therapeutics for their safe use in humans. Flavonoids, a group of polyphenols, have drawn great interest for their various health benefits, and have been identified in naturally occurring anti-diabetic compounds. Results from many clinical and animal studies demonstrate that dietary intake of flavonoids might prove helpful in preventing T2D. In this review, we discuss the currently available rodent animal models of T2D and analyze the advantages, the limitations of each T2D model, and highlight the potential anti-diabetic effects of flavonoids as well as the mechanisms of their actions.
Keywords: animal model; antioxidant; flavonoid; type 2 diabetes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, and in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

