Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. Extract Attenuate UVB-Induced Photoaging through MAPK/AP-1 Inactivation in Human Skin Fibroblasts and Hairless Mice
- PMID: 30823635
- PMCID: PMC6470489
- DOI: 10.3390/nu11030533
Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. Extract Attenuate UVB-Induced Photoaging through MAPK/AP-1 Inactivation in Human Skin Fibroblasts and Hairless Mice
Abstract
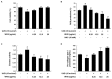
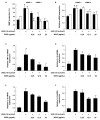
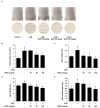
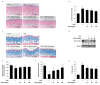
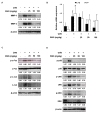
Skin photoaging is mainly caused by exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light, which increases expressions of matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and destroys collagen fibers, consequently inducing wrinkle formation. Nutritional factors have received scientific attention for use as agents for normal skin functions. The aim of this study was to investigate the effect of hot water extracts from the leaves of Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser. (WHS) against ultraviolet B (UVB)-induced skin photoaging and to elucidate the underlying molecular mechanisms in human foreskin fibroblasts (Hs68) and HR-1 hairless mice. WHS recovered UVB-reduced cell viability and ameliorated oxidative stress by inhibiting intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation in Hs68 cells. WHS rescued UVB-induced collagen degradation by suppressing MMP expression, and reduced the mRNA levels of inflammatory cytokines. These anti-photoaging activities of WHS were associated with inhibition of the activator protein 1 (AP-1), signal transduction and activation of transcription 1 (STAT1), and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathways. Oral administration of WHS effectively alleviated dorsal skin from wrinkle formation, epidermal thickening, collagen degradation, and skin dehydration in HR-1 hairless mice exposed to UVB. Notably, WHS suppressed UVB activation of the AP-1 and MAPK signaling pathways in dorsal mouse skin tissues. Taken together, our data indicate that WHS prevents UVB-induced skin damage due to collagen degradation and MMP activation via inactivation of MAPK/AP-1 signaling pathway.
Keywords: AP-1; Hydrangea serrata (Thunb.) Ser.; MAPK; MMPs; collagen; photoaging; ultraviolet B.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Bosch R., Philips N., Suarez-Perez J.A., Juarranz A., Devmurari A., Chalensouk-Khaosaat J., Gonzalez S. Mechanisms of Photoaging and Cutaneous Photocarcinogenesis, and Photoprotective Strategies with Phytochemicals. Antioxidants (Basel) 2015;4:248–268. doi: 10.3390/antiox4020248. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

