Incidence and determinants of diabetes-related lower limb amputations in Ghana, 2010-2015- a retrospective cohort study
- PMID: 30823912
- PMCID: PMC6397489
- DOI: 10.1186/s12902-019-0353-8
Incidence and determinants of diabetes-related lower limb amputations in Ghana, 2010-2015- a retrospective cohort study
Abstract
Background: Diabetes-related lower limb amputations (LLA) are associated with significant morbidity and mortality. Although the incidence has decreased over the past two decades in most High-Income Countries, the situation in Low-Middle Income Countries (LMIC), especially those in sub-Saharan Africa (SSA) is not clear. We have determined the incidence and determinants of diabetes-related LLA in Ghana.
Methods: This was a tertiary-care-based retrospective cohort study involving patients enrolled in the diabetes clinic of Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital, Ghana from 1st January 2010 to 31st December 2015 after a median follow-up of 4.2 years. Demographic characteristics and clinical variables at baseline were recorded. The primary outcome was new diabetes-related LLA in each year under study. Cox proportional hazard regression models were used to describe the associations of diabetes-related LLA.
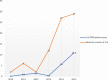
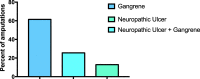
Results: The mean age at enrolment for the cohort was 55.9 ± 14.6 years, with a female preponderance (62.1%). The average incidence rate of diabetes-related LLA was 2.4 (95% CI:1.84-5.61) per 1000 follow-up years: increasing from 0.6% (95% CI:0.21-2.21) per 1000 follow up years in 2010 to 10.9% (95% CI:6.22-12.44) per 1000 follow-up years in 2015. Diabetes-related LLA was associated with increased age at enrollment (for every 10 year increase in age: HR: 1.11, CI: 1.06-1.22, p < 0.001), male gender (HR: 3.50, CI:2.88-5.23, p < 0.01), type 2 diabetes (HR 3.21, CI: 2.58-10.6, p < 0.001), high Body Mass Index (HR: 3.2, CI: 2.51-7.25 p < 0.001), poor glycemic control (for a percent increase in HbA1c, HR:1.11, CI:1.05-1.25, p = 0.03), hypertension (HR:1.14, CI:1.12-3.21 p < 0.001), peripheral sensory neuropathy (HR:6.56 CI:6.21-8.52 p < 0.001) and peripheral vascular disease (HR: 7.73 CI: 4.39-9.53, p < 0.001).
Conclusion: The study confirms a high incidence of diabetes related-LLA in Ghana. Interventions aimed at addressing systemic and patient-level barriers to good vascular risk factor control and proper foot care for diabetics should be introduced in LMICs to stem the tide of the increasing incidence of LLA.
Keywords: Diabetes; Ghana; Lower limb amputation.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Committee on Human Research Publication and Ethics of the School of Medical Sciences, Kwame Nkrumah University of Science and Technology, and the Komfo Anokye Teaching Hospital, Kumasi. We anonymised patient’s records/information before analysis.
Consent for publication
Not applicable on request.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous