L-Type Cav 1.2 Calcium Channel-α-1C Regulates Response to Rituximab in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 30824586
- PMCID: PMC9161643
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2146
L-Type Cav 1.2 Calcium Channel-α-1C Regulates Response to Rituximab in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
Purpose: One third of patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) succumb to the disease partly due to rituximab resistance. Rituximab-induced calcium flux is an important inducer of apoptotic cell death, and we investigated the potential role of calcium channels in rituximab resistance.
Experimental design: The distinctive expression of calcium channel members was compared between patients sensitive and resistant to rituximab, cyclophosphamide, vincristine, doxorubicin, prednisone (RCHOP) regimen. The observation was further validated through mechanistic in vitro and in vivo studies using cell lines and patient-derived xenograft mouse models.
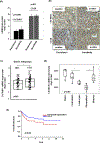
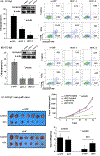
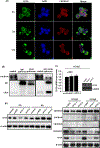
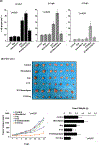
Results: A significant inverse correlation was observed between CACNA1C expression and RCHOP resistance in two independent DLBCL cohorts, and CACNA1C expression was an independent prognostic factor for RCHOP resistance after adjusting for International Prognostic Index, cell-of-origin classification, and MYC/BCL2 double expression. Loss of CACNA1C expression reduced rituximab-induced apoptosis and tumor shrinkage. We further demonstrated direct interaction of CACNA1C with CD20 and its role in CD20 stabilization. Functional modulators of L-type calcium channel showed expected alteration in rituximab-induced apoptosis and tumor suppression. Furthermore, we demonstrated that CACNA1C expression was directly regulated by miR-363 whose high expression is associated with worse prognosis in DLBCL.
Conclusions: We identified the role of CACNA1C in rituximab resistance, and modulating its expression or activity may alter rituximab sensitivity in DLBCL.
©2019 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Rituximab in the treatment of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: The CACNA1C subunit of channel Cav1.2 expression linked to certain forms of resistance].Med Sci (Paris). 2021 Apr;37(4):406-408. doi: 10.1051/medsci/2021043. Epub 2021 Apr 28. Med Sci (Paris). 2021. PMID: 33908862 French. No abstract available.
-
DLBCL developed into fatal liver failure during rituximab-containing chemotherapy.J Clin Exp Hematop. 2019;59(2):93-95. doi: 10.3960/jslrt.19004. J Clin Exp Hematop. 2019. PMID: 31257349 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 4-mediated metabolic reprogramming is involved in rituximab resistance in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by affecting the expression of MS4A1/CD20.Cancer Sci. 2021 Sep;112(9):3585-3597. doi: 10.1111/cas.15055. Epub 2021 Jul 28. Cancer Sci. 2021. PMID: 34252986 Free PMC article.
-
The Spectrum of MYC Alterations in Diffuse Large B-Cell Lymphoma.Acta Haematol. 2020;143(6):520-528. doi: 10.1159/000505892. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Acta Haematol. 2020. PMID: 32074595 Review.
-
Hitting back at lymphoma: How do modern diagnostics identify high-risk diffuse large B-cell lymphoma subsets and alter treatment?Cancer. 2019 Sep 15;125(18):3111-3120. doi: 10.1002/cncr.32145. Epub 2019 Jul 9. Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31287161 Review.
Cited by
-
Calcium channelopathies and intellectual disability: a systematic review.Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021 May 13;16(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s13023-021-01850-0. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2021. PMID: 33985586 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-regulated secretion of IL-12 enhances antitumor activity and safety of CD19 CAR-T cells in the treatment of DLBCL.Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2023 Aug 18;30:216-226. doi: 10.1016/j.omto.2023.08.009. eCollection 2023 Sep 21. Mol Ther Oncolytics. 2023. PMID: 37663131 Free PMC article.
-
Combinatorial protection of cochlear hair cells: not too little but not too much.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Sep 17;18:1458720. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1458720. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39355176 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-363-3p/DUSP10/JNK axis mediates chemoresistance by enhancing DNA damage repair in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma.Leukemia. 2022 Jul;36(7):1861-1869. doi: 10.1038/s41375-022-01565-6. Epub 2022 Apr 29. Leukemia. 2022. PMID: 35488020 Free PMC article.
-
Connecting Calcium-Based Nanomaterials and Cancer: From Diagnosis to Therapy.Nanomicro Lett. 2022 Jul 18;14(1):145. doi: 10.1007/s40820-022-00894-6. Nanomicro Lett. 2022. PMID: 35849180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lossos IS, Morgensztern D. Prognostic biomarkers in diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2006;24:995–1007. - PubMed
-
- Iqbal J, Naushad H, Bi C, Yu J, Bouska A, Rohr J, et al. Genomic signatures in B-cell lymphoma: How can these improve precision in diagnosis and inform prognosis? Blood Rev 2016;30:73–88. - PubMed
-
- Coiffier B, Thieblemont C, Van Den Neste E, Lepeu G, Plantier I, Castaigne S, et al. Long-term outcome of patients in the LNH-98.5 trial, the first randomized study comparing rituximab-CHOP to standard CHOP chemotherapy in DLBCL patients: a study by the Groupe d’Etudes des Lymphomes de l’Adulte. Blood 2010;116:2040–5. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davis TA, Grillo-Lopez AJ, White CA, McLaughlin P, Czuczman MS, Link BK, et al. Rituximab anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy in non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma: safety and efficacy of re-treatment. J Clin Oncol 2000;18:3135–43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

