Prioritizing Parkinson's disease genes using population-scale transcriptomic data
- PMID: 30824768
- PMCID: PMC6397174
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-08912-9
Prioritizing Parkinson's disease genes using population-scale transcriptomic data
Abstract
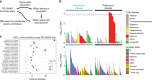
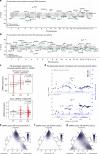
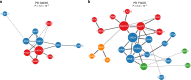
Genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified over 41 susceptibility loci associated with Parkinson's Disease (PD) but identifying putative causal genes and the underlying mechanisms remains challenging. Here, we leverage large-scale transcriptomic datasets to prioritize genes that are likely to affect PD by using a transcriptome-wide association study (TWAS) approach. Using this approach, we identify 66 gene associations whose predicted expression or splicing levels in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLFPC) and peripheral monocytes are significantly associated with PD risk. We uncover many novel genes associated with PD but also novel mechanisms for known associations such as MAPT, for which we find that variation in exon 3 splicing explains the common genetic association. Genes identified in our analyses belong to the same or related pathways including lysosomal and innate immune function. Overall, our study provides a strong foundation for further mechanistic studies that will elucidate the molecular drivers of PD.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- R01 AG054005/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R37 MH057881/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH075916/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG017917/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD018522/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH084053/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN271201300031C/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 MH066392/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH080405/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG036042/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG046152/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036042/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG010161/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH097276/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 AG036547/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AG002219/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH093725/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P50 AG005138/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG036836/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH085542/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG015819/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

