Efficacy of topical clotrimazole vs. topical tolnaftate in the treatment of otomycosis. A randomized controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 30826311
- PMCID: PMC9422661
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2018.12.007
Efficacy of topical clotrimazole vs. topical tolnaftate in the treatment of otomycosis. A randomized controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Introduction: Otomycosis, an infection of the ear canal by fungi, is prevalent in hot and humid weather. Nevertheless, there is not sufficient evidence for the effectiveness of different topical antifungal treatments. Tolnaftate, is a topical antifungal agent described to be effective in the treatment of otomycosis. Currently there are not sufficient studies that prove its efficacy.
Objectives: To compare the efficacy of clotrimazole and tolnaftate administration in the treatment of otomycosis.
Material and methods: A controlled, randomized and open clinical trial included patients diagnosed with fungal external otitis who were treated with topical antifungals, randomized into two treatment groups: (1) clotrimazole cream; (2) tolnaftate solution. They were microscopically evaluated at one and two weeks of treatment to determine resolution of disease. Recurrence and complications were recorded. Demographic and clinical variables were collected and analyzed. Follow-up and final outcomes (absence of infection) were compared between groups.
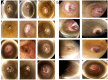
Results: Forty eight patients were included, 28 in the clotrimazole group and 20 in the tolnaftate group. Spring was the weather most commonly associated with otomycosis, while otic manipulation was the risk factor more common in both groups. Predominant symptoms were itching and otic fullness. Aspergillus niger organism was isolated most frequently. Treatment with clotrimazole resulted in 75% resolution vs 45% resolution with treatment with tolnaftate at one week of treatment (p=0.007). The Tolnaftate treatment group demonstrated higher recurrence rates and treatment failures, 20% and 15% respectively.
Conclusions: Clotrimazole cream treatment is more effective than tolnaftate for uncomplicated otomycosis. More studies are needed to corroborate our results.
Introdução: Otomicose, uma infecção fúngica do canal auditivo externo, é prevalente em climas quentes e úmidos. No entanto, a literatura não apresenta evidências suficientes sobre os diferentes tratamentos antifúngicos tópicos. O tolnaftato é um antifúngico tópico descrito como eficaz no tratamento da otomicose; entretanto, sua eficácia não está suficientemente comprovada.
Objetivo: Comparar a eficácia do uso de clotrimazol e tolnaftato no tratamento da otomicose.
Material e método: Ensaio clínico controlado e randomizado; incluiu pacientes diagnosticados com otite externa fúngica tratados com antifúngicos tópicos, randomizados em dois grupos de tratamento: 1) clotrimazole (creme); 2) solução de tolnaftato. Eles foram avaliados microscopicamente uma e duas semanas após o início do tratamento para avaliar a resolução da doença. Recorrência e intercorrências foram registradas; além disso, as variáveis demográficas e clínicas foram coletadas e analisadas. Os dados do acompanhamento e desfechos finais (ausência de infecção) foram comparados entre os grupos.
Resultados: O estudo incluiu 48 pacientes, 28 dos quais foram alocados ao grupo clotrimazole e 20 ao grupo tolnaftato. A primavera foi a estação mais comum; a manipulação foi o fator de risco mais comum em ambos os grupos. Os sintomas mais comuns foram coceira e plenitude auricular. Aspergillus niger foi o micro-organismo mais comumente isolado. Após uma semana, o tratamento com clotrimazol apresentou uma taxa de resolução de 75% vs. 45% com o tratamento com tolnaftato (p = 0,007). O tratamento com tolnaftato apresentou maiores taxas de recidiva e falhas: 20% e 15%, respectivamente.
Conclusões: Em casos de otomicose não complicada, o uso de clotrimazol (creme) é mais eficaz do que o de tolnaftato. Mais estudos são necessários para corroborar os presentes resultados.
Keywords: Antifungals; Antifúngicos; Clotrimazole (creme); Clotrimazole cream; Otomicoses; Otomycosis; Tolnaftato tópico; Topical tolnaftate.
Copyright © 2019 Associação Brasileira de Otorrinolaringologia e Cirurgia Cérvico-Facial. Published by Elsevier Editora Ltda. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Kaieda S. Fungal infection in the otorinolaryngologic area. Nihon Rinsho. 2008;66:2290–2293. - PubMed
-
- Ho T., Vraben J., Yoo D., Coker N. Otomycosis: clinical features and treatment implications. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;135:787–791. - PubMed
-
- Vega-Nava C.T., Borrego-Montoya C.R., Vásquez-Del Mercado E., Vega-Sánchez D.C., Arenas R. Otitis externa de origen fúngico. Estudio de 36 pacientes en un hospital general. An Orl Mex. 2015;60:175–178.
-
- Linstrom C., Lucente F. In: Head & neck surgery-otolaryngology. Bailey J., Johnson T., Newlands D., editors. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins; Philadelphia, PA: 2014. Diseases of the external ear; pp. 1987–2002.
-
- Rosenfeld R.M., Brown L., Cannon C.R., Dolor R.J., Ganiats T.G., Hannley M., et al. Clinical practice guideline: acute otitis externa. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;134:S4–S23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

