T-cell mitochondrial dysfunction and lymphopenia in DOCK2-deficient patients
- PMID: 30826364
- PMCID: PMC6612298
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.02.020
T-cell mitochondrial dysfunction and lymphopenia in DOCK2-deficient patients
Abstract
This study delineates the mitochondrial defects in DOCK2-deficient T cells contributing to the T cell lymphopenia characteristic of this primary immunodeficiency.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
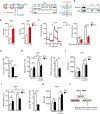
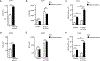
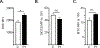
References
-
- Nishihara H, Maeda M, Tsuda M, Makino Y, Sawa H, Nagashima K, et al. DOCK2 mediates T cell receptor-induced activation of Rac2 and IL-2 transcription. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002;296:716–20. - PubMed
-
- Alizadeh Z, Mazinani M, Shakerian L, Nabavi M, Fazlollahi MR. DOCK2 Deficiency in a Patient with Hyper IgM Phenotype. J Clin Immunol 2018;38:10–2. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

