Pembrolizumab-induced Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia and Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 30828042
- PMCID: PMC6443545
- DOI: 10.2169/internalmedicine.1001-18
Pembrolizumab-induced Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia and Hemophagocytic Lymphohistiocytosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
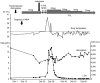
We herein report a 78-year old man with squamous cell carcinoma of the lungs treated with pembrolizumab. At 10 days after the administration of pembrolizumab, he showed progressive anemia and increased levels of bilirubin. Because the findings of a direct coombs test and cold hemagglutinin were positive, we diagnosed the patient with autoimmune hemolytic anemia and treated him with prednisolone. Subsequently, he was admitted to our hospital owing to fatigue, a high fever, and jaundice. His clinical findings met the diagnostic criteria of hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis, and he was rescued with a high dose of glucocorticoids. Marked tumor regression was obtained and has been maintained since then.
Keywords: autoimmune hemolytic anemia; hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis; immune checkpoint inhibitors; non-small cell lung cancer; pembrolizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Reck M, Rodríguez-Abreu D, Robinson AG, et al. . Pembrolizumab versus chemotherapy for PD-L1-positive non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med 375: 1823-1833, 2016. - PubMed
-
- Henter JI, Horne A, Aricó M, et al. . Diagnostic and therapeutic guidelines for hemophagocytic lymphohistiocytosis. Pediatr Blood Cancer 48: 124-131, 2007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

