Safe corridor for fibular transfixation wire in relation to common peroneal nerve: A cadaveric analysis
- PMID: 30828221
- PMCID: PMC6383134
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jcot.2018.05.002
Safe corridor for fibular transfixation wire in relation to common peroneal nerve: A cadaveric analysis
Erratum in
-
Erratum regarding previously published articles.J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020 Nov-Dec;11(6):1169-1171. doi: 10.1016/j.jcot.2020.09.032. Epub 2020 Sep 26. J Clin Orthop Trauma. 2020. PMID: 33013141 Free PMC article.
Abstract
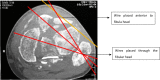
Background: Peroneal nerve impalement is a recognized complication of percutaneous placement of fibular transfixation wires by palpatory method after increase use of ilizarov technique in treatment of Tibial fractures, deformity correction and limb lengthening. The purpose of this study was to identify the relationship between the Common Peroneal Nerve (CPN) and the palpable landmark, fibular head for insertion of proximal fibular transfixation wire, safe zones in proximal tibia and percentage of fibula where nerve crosses the neck.
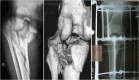
Methods: Standard 1.8-mm Ilizarov k- wires were inserted in the fibula head of fresh 10 un-embalmed cadaveric knees. Wires were inserted percutaneously to the fibula head by palpatory technique. The course of common peroneal nerve was dissected. Distances from wire entry point to the course of the common peroneal nerve were measured post-wire insertion.
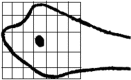
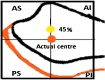
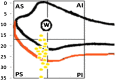
Results: The mean distance of the common peroneal nerve from the anterior aspect of the broadest point of the fibular head was 25.10 ± 4.39 mm (range 16-35 mm). Common peroneal nerve was seen to cross the neck of fibula at a mean distance of 32.3 ± 8.53 mm (range 20-50 mm). Wire placement was found to be on average, 46% of the maximal AP diameter of the fibula head and 44% of the distance from tip of fibula to the point of nerve crossing fibula neck.
Conclusion: We recommend Proximal fibula transfixation wires are safer to pass with in 2 cm from the tip of the styloid process of the fibula, Anterior half of the head of fibula, <8% of total fibular length, Ventral half of the anterior compartment to avoid injury to peroneal fan. The palpable landmark of fibula is a misinterpretation; it is just the prominent subcutaneous portion of fibula and not the styloid process of fibula which on dissection was located much posterior. Better to take fluoroscopic guidance in difficult cases where palpation of head of fibula is difficult.
Keywords: Common peroneal nerve; Fibula transfixation wire; Ilizarov fixation; Safe corridor.
Figures










References
-
- Rudloff M. Fractures of the lower extremity. In: Daugherty K., Jones L., editors. Campbell’s operative orthopaedics. 12th ed. Elseiver Mosby; Canada: 2013. p. 2681.
-
- Kataria H., Sharma N., Kanojia R. Small wire external fixation for high-energy tibial plateau fractures. J Orthop Surg. 2007;15(2):137–143. - PubMed
-
- Ali A., Burton M., Hashmi M., Saleh M. Outcome of complex fractures of the tibial plateau treated with beam-loading ring fixation system. J Bone Jt Surg (Br) 2003;85-B:691–699. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

