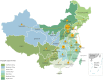
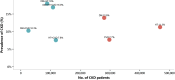
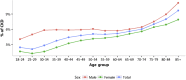
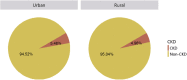
China Kidney Disease Network (CK-NET) 2015 Annual Data Report
- PMID: 30828481
- PMCID: PMC6382959
- DOI: 10.1016/j.kisu.2018.11.001
China Kidney Disease Network (CK-NET) 2015 Annual Data Report
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum to "Zhang L, Zhao M-H, Zuo L, et al., on behalf of CK-NET Group. China Kidney Disease Network (CK-NET) 2015 Annual Data Report." Kidney Int Suppl. 2019;9:e1-e81.Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2020 Mar;10(1):e95. doi: 10.1016/j.kisu.2019.05.001. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2020. PMID: 32195037 Free PMC article.
Figures





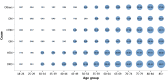
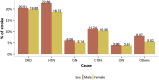

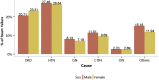

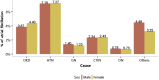








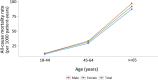
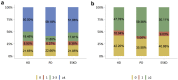
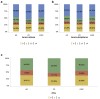
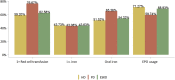


References
-
- Fried L.F., Emanuele N., Zhang J.H. Combined angiotensin inhibition for the treatment of diabetic nephropathy. N Engl J Med. 2013;369:1892–1903. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

