Chemoradiotherapy-Induced CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Alterations to Predict Patient Outcomes in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 30828566
- PMCID: PMC6385789
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00073
Chemoradiotherapy-Induced CD4+ and CD8+ T-Cell Alterations to Predict Patient Outcomes in Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
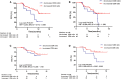
Purpose and Objectives: Chemoradiotherapy (CRT) is an important component of treatment for patients with locally advanced esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC). Recent research findings support the role of CRT in activating an anti-tumor immune response. However, predictors of CRT efficacy are not fully understood. The aim of this study was to measure CRT-induced changes to lymphocyte subpopulations and to evaluate the prognostic value of lymphocyte alterations for patients with ESCC. Materials and Methods: In total, this pilot study enrolled 64 patients with ESCC who received neo-adjuvant CRT or definitive CRT. Peripheral blood samples were collected before and during treatment and were analyzed by flow cytometry for CD19, CD3, CD4, CD8, CD56, and CD16. Relationships between lymphocyte subset alterations and overall survival (OS) and progression-free survival (PFS) were evaluated using the log-rank test and a Cox regression model. Results: The median follow-up period was 11.8 months (range, 4.0-20.2 months). Compared to pre-treatment specimens, post-treatment blood samples had decreased proportions of CD19+ B-cells and increased proportions of CD3+ and CD8+ T-cells (all P < 0.05). Univariate and multivariate analysis showed that increased CD4+ T-cell ratios after CRT independently predicted superior PFS (hazard ratio [HR] = 0.383; 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.173-0.848, P = 0.017) and that increased CD8+ T-cell ratios predicted improved OS (HR = 0.258; 95% CI = 0.083-0.802, P = 0.019). Patients with both increased CD4+ and CD8+ ratios had a superior PFS and OS, compared to patients with an increased CD4+ ratio only or CD8+ ratio only or neither (1-year PFS rate 63 vs. 25%, 1-year OS rate 80 vs. 62%, P = 0.005 and 0.025, respectively). Conclusions: CRT-induced increases in CD4+ and CD8+ T-cell ratios are reliable biomarker predictors of survival in patients with ESCC.
Keywords: CD4+ T-cell; CD8+ T-cell; chemoradiotherapy; clinical outcomes; esophageal squamous cell carcinoma.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

