Thermistor-controlled subdermal skin tightening for the aging face: Clinical outcomes and efficacy
- PMID: 30828614
- PMCID: PMC6383317
- DOI: 10.1002/lio2.228
Thermistor-controlled subdermal skin tightening for the aging face: Clinical outcomes and efficacy
Abstract
Objective: Patients are increasingly seeking nonsurgical treatment for the aging face. The purpose of this study was to evaluate the clinical efficacy and outcomes of a thermistor-controlled subdermal skin tightening device (ThermiTight) as a treatment modality for the aging face.
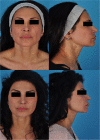
Methods: A retrospective analysis of 12 patients was completed on patients having undergone ThermiTight for midface and neck skin tightening. Only five patients had a greater than 1 year follow-up and were included in the study. Two blinded reviewers assessed photographs taken pre-procedure and 1 year post-procedure using a standardized skin laxity scale. Patient charts were reviewed to assess for complications up to 12 months post-treatment.
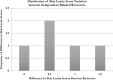
Results: The mean age of included patients was 57 years, and all five patients were female. One (20%) patient treated with ThermiTight was also treated with injectables (Botox, Juvéderm) simultaneously. One (20%) patient developed a wound complication. One (20%) patient complained of incisional site pain at her first postoperative visit that subsequently self-resolved. On a five-point scale to assess facial skin laxity, there was an average improved score of 0.85 per patient (P < .001) at one year post-procedure. Two blinded reviewers correctly categorized photographs as either being "baseline" or "post-procedure" 100% of the time. There was no significant difference between the skin laxity scores by the blinded reviewers (P = .05).
Conclusion: ThermiTight is a new technology used for nonsurgical treatment of the aging face. Long-term outcomes demonstrate the safety and efficacy of the procedure. Complications are rare, but possible, in the use of ThermiTight. Level of Evidence: 3.
Keywords: ThermiTight; Thermistor; aesthetic surgery; aging face; injectable; skin laxity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Integration of thermal imaging with subsurface radiofrequency thermistor heating for the purpose of skin tightening and contour improvement: a retrospective review of clinical efficacy.J Drugs Dermatol. 2014 Dec;13(12):1485-9. J Drugs Dermatol. 2014. PMID: 25607794
-
Evaluation of a microfocused ultrasound system for improving skin laxity and tightening in the lower face.Aesthet Surg J. 2014 Sep;34(7):1099-110. doi: 10.1177/1090820X14541956. Epub 2014 Jul 2. Aesthet Surg J. 2014. PMID: 24990884 Clinical Trial.
-
Subdermal Radiofrequency for Skin Tightening of the Posterior Upper Arms.Dermatol Surg. 2016 Sep;42(9):1089-93. doi: 10.1097/DSS.0000000000000842. Dermatol Surg. 2016. PMID: 27560292
-
Percutaneous Radiofrequency Technologies for the Lower Face and Neck.Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2019 Aug;27(3):305-320. doi: 10.1016/j.fsc.2019.03.003. Epub 2019 May 16. Facial Plast Surg Clin North Am. 2019. PMID: 31280845 Review.
-
Microfocused ultrasound for skin tightening.Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013 Mar;32(1):18-25. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2013. PMID: 24049925 Review.
Cited by
-
Transcutaneous Temperature Controlled Radiofrequency: Groundbreaking Technology - Female Stress Urinary Incontinence and Overactive Bladder Can Be Treated Noninvasively and with Vulvovaginal Rejuvenation?J Midlife Health. 2023 Apr-Jun;14(2):69-72. doi: 10.4103/jmh.jmh_19_23. Epub 2023 Sep 18. J Midlife Health. 2023. PMID: 38029027 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Relevance of Skin Tightening with Minimally Invasive Subdermal Energy-Based (EB) Technologies.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025 Jun 27. doi: 10.1007/s00266-025-05022-4. Online ahead of print. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2025. PMID: 40576814 Review.
-
Regenerative Synergy: Combining Platelet-rich Plasma with Transcutaneous Temperature-controlled Radiofrequency for Enhanced Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence in Peri- and Postmenopausal Women.J Midlife Health. 2025 Apr-Jun;16(2):179-185. doi: 10.4103/jmh.jmh_34_25. Epub 2025 Jun 23. J Midlife Health. 2025. PMID: 40636837 Free PMC article.
-
Comment on: Safety and Effectiveness of Endodermal Radiofrequency for Skin Rejuvenation: A Systematic Review.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024 Jan;48(1):4-7. doi: 10.1007/s00266-022-03148-3. Epub 2022 Oct 24. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2024. PMID: 36278992 No abstract available.
-
Safety and Effectiveness of Endodermal Radiofrequency for Skin Rejuvenation: A Systematic Review.Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2023 Feb;47(1):378-386. doi: 10.1007/s00266-022-03097-x. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 2023. PMID: 36178511
References
-
- Dibernardo Be. The aging neck: a diagnostic approach to surgical and nonsurgical options. J Cosmet Laser Ther 2013;14(2):56–64. - PubMed
-
- Mitz V, Peyronie M. The superficial musculo‐aponeurotic system (SMAS) in the parotid and cheek area. Plast Reconstr Surg 1976;58(1):80–88. - PubMed
-
- Ahn DH, Mulholland RS, Diane D, Malcolm P. Non‐excisional face and neck tightening using a novel subdermal radio‐frequency thermo‐coagulative device. JCDSA 2011;4(1):141–146.
-
- Camile H, Doris H, Manolea DP, Juliana S, Carolina S. Botulinum toxin type A for aging face and aesthetic uses. Dermatol Ther 2011;24(1):54–61. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
