The nonconservative CD177 single-nucleotide polymorphism c.1291G>A is a genetic determinant for human neutrophil antigen-2 atypical/low expression and deficiency
- PMID: 30828823
- PMCID: PMC6499709
- DOI: 10.1111/trf.15222
The nonconservative CD177 single-nucleotide polymorphism c.1291G>A is a genetic determinant for human neutrophil antigen-2 atypical/low expression and deficiency
Abstract
Background: Human neutrophil antigen-2 (HNA-2) is exclusively expressed on neutrophils. HNA-2-deficient individuals (HNA-2 null) are susceptible to produce isoantibodies. The nonsense CD177 coding single-nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) c.787A>T has been demonstrated as the primary genetic mechanism for HNA-2 deficiency. We hypothesized that the other genetic variants also contribute to HNA-2 expression variation and deficiency.
Study design and methods: The deficiency, density, and percentage of HNA-2 antigen on neutrophils from 292 healthy blood donors were determined in flow cytometry. CD177 genotypes were determined by genomic DNA sequence analyses. The full-length CD177 cDNAs were amplified and sequenced. Additionally, the whole CD177 genomic sequence in eight HNA-2-null immunized women and four HNA-2-positive donors were analyzed with next-generation sequencing. The associations of CD177 SNP genotypes with HNA-2 expression variation were statistically analyzed.
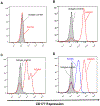
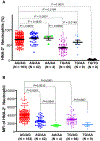
Results: A functional CD177 SNP c.1291G>A was identified in the current study. Atypical (trimodal) HNA-2 expression phenotype was consistently observed in donors carrying the heterozygous c.1291G/A genotype. Phenotype-genotype analyses of SNP c.787A>T and SNP c.1291G>A revealed that all homozygous 787T-1291G (TG/TG) genotype donors were HNA-2 null in healthy blood donors. On the other hand, five of eight HNA-2-immunized females were homozygous for the 787T-1291G (TG/TG) genotype while the other three HNA-2-immunized females had the 787T-1291G/787A-1291A (TG/AA) genotype and the lowest HNA-2 expression was observed in healthy subjects with the 787T-1291G/787A-1291A (TG/AA) and 787A-1291A/787A-1291A (AA/AA) genotype.
Conclusion: The CD177 SNP c.1291G>A is a genetic determinant for the atypical and low HNA-2 expression, which also contributes to HNA-2 deficiency phenotype.
© 2019 AABB.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Kissel K, Santoso S, Hofmann C, Stroncek D, Bux J. Molecular basis of the neutrophil glycoprotein NB1 (CD177) involved in the pathogenesis of immune neutropenias and transfusion reactions. Eur J Immunol 2001;31: 1301–9. - PubMed
-
- Bettinotti MP, Olsen A, Stroncek D. The use of bioinformatics to identify the genomic structure of the gene that encodes neutrophil antigen NB1, CD177. Clin Immunol 2002;102: 138–44. - PubMed
-
- Caruccio L, Bettinotti M, Director-Myska AE, Arthur DC, Stroncek D. The gene overexpressed in polycythemia rubra vera, PRV-1, and the gene encoding a neutrophil alloantigen, NB1, are alleles of a single gene, CD177, in chromosome band 19q13.31. Transfusion 2006;46: 441–7. - PubMed
-
- Temerinac S, Klippel S, Strunck E, Roder S, Lubbert M, Lange W, Azemar M, Meinhardt G, Schaefer HE, Pahl HL. Cloning of PRV-1, a novel member of the uPAR receptor superfamily, which is overexpressed in polycythemia rubra vera. Blood 2000;95: 2569–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

