RAF dimers control vascular permeability and cytoskeletal rearrangements at endothelial cell-cell junctions
- PMID: 30828992
- PMCID: PMC6617973
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.14802
RAF dimers control vascular permeability and cytoskeletal rearrangements at endothelial cell-cell junctions
Abstract
The endothelium functions as a semipermeable barrier regulating fluid homeostasis, nutrient, and gas supply to the tissue. Endothelial permeability is increased in several pathological conditions including inflammation and tumors; despite its clinical relevance, however, there are no specific therapies preventing vascular leakage. Here, we show that endothelial cell-restricted ablation of BRAF, a kinase frequently activated in cancer, prevents vascular leaking as well metastatic spread. BRAF regulates endothelial permeability by promoting the cytoskeletal rearrangements necessary for the remodeling of VE-Cadherin-containing endothelial cell-cell junctions and the formation of intercellular gaps. BRAF kinase activity and the ability to form complexes with RAS/RAP1 and dimers with its paralog RAF1 are required for proper permeability control, achieved mechanistically by modulating the interaction between RAF1 and the RHO effector ROKα. Thus, RAF dimerization impinges on RHO pathways to regulate cytoskeletal rearrangements, junctional plasticity, and endothelial permeability. The data advocate the development of RAF dimerization inhibitors, which would combine tumor cell autonomous effect with stabilization of the vasculature and antimetastatic spread.
Keywords: RAF kinases; cell-cell adhesions; cytoskeletal rearrangements; vascular permeability.
© 2019 The Authors. The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
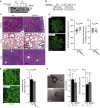


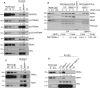

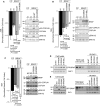


Comment in
-
BRAF, A gatekeeper controlling endothelial permeability.FEBS J. 2019 Jun;286(12):2273-2276. doi: 10.1111/febs.14861. Epub 2019 May 13. FEBS J. 2019. PMID: 31081213
References
-
- Trani M & Dejana E (2015) New insights in the control of vascular permeability: vascular endothelial‐cadherin and other players. Curr Opin Hematol 22, 267–272. - PubMed
-
- Kreuger J & Phillipson M (2016) Targeting vascular and leukocyte communication in angiogenesis, inflammation and fibrosis. Nat Rev Drug Discov 15, 125–142. - PubMed
-
- Nguyen DX, Bos PD & Massague J (2009) Metastasis: from dissemination to organ‐specific colonization. Nat Rev Cancer 9, 274–284. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

