Chronic, Intermittent Microdoses of the Psychedelic N, N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) Produce Positive Effects on Mood and Anxiety in Rodents
- PMID: 30829033
- PMCID: PMC6639775
- DOI: 10.1021/acschemneuro.8b00692
Chronic, Intermittent Microdoses of the Psychedelic N, N-Dimethyltryptamine (DMT) Produce Positive Effects on Mood and Anxiety in Rodents
Abstract
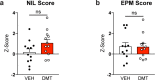
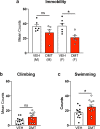
Drugs capable of ameliorating symptoms of depression and anxiety while also improving cognitive function and sociability are highly desirable. Anecdotal reports have suggested that serotonergic psychedelics administered in low doses on a chronic, intermittent schedule, so-called "microdosing", might produce beneficial effects on mood, anxiety, cognition, and social interaction. Here, we test this hypothesis by subjecting male and female Sprague Dawley rats to behavioral testing following the chronic, intermittent administration of low doses of the psychedelic N,N-dimethyltryptamine (DMT). The behavioral and cellular effects of this dosing regimen were distinct from those induced following a single high dose of the drug. We found that chronic, intermittent, low doses of DMT produced an antidepressant-like phenotype and enhanced fear extinction learning without impacting working memory or social interaction. Additionally, male rats treated with DMT on this schedule gained a significant amount of body weight during the course of the study. Taken together, our results suggest that psychedelic microdosing may alleviate symptoms of mood and anxiety disorders, though the potential hazards of this practice warrant further investigation.
Keywords: DMT; PTSD; Psychedelic; anxiety; depression; microdosing; neural plasticity; subhallucinogenic.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures



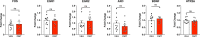
References
-
- U.S. National Library of Medicine . Depression: How effective are antidepressants? https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0087089/ (accessed October 2018).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

