A comparison of antigen-specific T cell responses induced by six novel tuberculosis vaccine candidates
- PMID: 30830940
- PMCID: PMC6417742
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1007643
A comparison of antigen-specific T cell responses induced by six novel tuberculosis vaccine candidates
Abstract
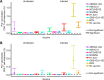
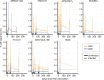
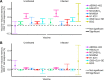
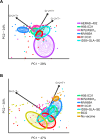
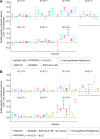
Eradication of tuberculosis (TB), the world's leading cause of death due to infectious disease, requires a highly efficacious TB vaccine. Many TB vaccine candidates are in pre-clinical and clinical development but only a few can be advanced to large-scale efficacy trials due to limited global resources. We aimed to perform a statistically rigorous comparison of the antigen-specific T cell responses induced by six novel TB vaccine candidates and the only licensed TB vaccine, Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG). We propose that the antigen-specific immune response induced by such vaccines provides an objective, data-driven basis for prioritisation of vaccine candidates for efficacy testing. We analyzed frequencies of antigen-specific CD4 and CD8 T cells expressing IFNγ, IL-2, TNF and/or IL-17 from adolescents or adults, with or without Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M.tb) infection, who received MVA85A, AERAS-402, H1:IC31, H56:IC31, M72/AS01E, ID93+GLA-SE or BCG. Two key response characteristics were analyzed, namely response magnitude and cytokine co-expression profile of the memory T cell response that persisted above the pre-vaccination response to the final study visit in each trial. All vaccines preferentially induced antigen-specific CD4 T cell responses expressing Th1 cytokines; levels of IL-17-expressing cells were low or not detected. In M.tb-uninfected and -infected individuals, M72/AS01E induced higher memory Th1 cytokine-expressing CD4 T cell responses than other novel vaccine candidates. Cytokine co-expression profiles of memory CD4 T cells induced by different novel vaccine candidates were alike. Our study suggests that the T cell response feature which most differentiated between the TB vaccine candidates was response magnitude, whilst functional profiles suggested a lack of response diversity. Since M72/AS01E induced the highest memory CD4 T cell response it demonstrated the best vaccine take. In the absence of immunological correlates of protection, the likelihood of finding a protective vaccine by empirical testing of candidates may be increased by the addition of candidates that induce distinct immune characteristics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organisation. Global tuberculosis report 2018. Geneva: 2018.
-
- Abu-Raddad LJ, Sabatelli L, Achterberg JT, Sugimoto JD, Longini IM, Dyee C, et al. Epidemiological benefits of more-effective tuberculosis vaccines, drugs, and diagnostics. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2009;106(33):13980–5. 10.1073/pnas.0901720106 PubMed Central PMCID: PMC19666590. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

