The specialised pro-resolving lipid mediator maresin 1 reduces inflammatory pain with a long-lasting analgesic effect
- PMID: 30830967
- PMCID: PMC6514290
- DOI: 10.1111/bph.14647
The specialised pro-resolving lipid mediator maresin 1 reduces inflammatory pain with a long-lasting analgesic effect
Abstract
Background and purpose: Maresin 1 (MaR1) is a specialised pro-resolving lipid mediator with anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities. In this study, we addressed the modulation of peripheral and spinal cord cells by MaR1 in the context of inflammatory pain.
Experimental approach: Mice were treated with MaR1 before intraplantar injection of carrageenan or complete Freund's adjuvant (CFA). Mechanical hyperalgesia was assessed using the electronic von Frey and thermal hyperalgesia using a hot plate. Spinal cytokine production and NF-κB activation were determined by ELISA and astrocytes and microglia activation by RT-qPCR and immunofluorescence. CGRP release by dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons was determined by EIA. Neutrophil and macrophage recruitment were determined by immunofluorescence, flow cytometry, and colorimetric methods. Trpv1 and Nav1.8 expression and calcium imaging of DRG neurons were determined by RT-qPCR and Fluo-4AM respectively.
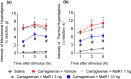
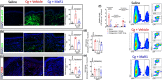
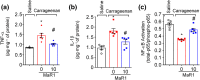
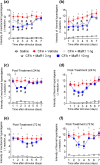
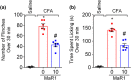
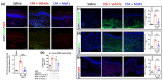
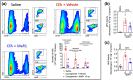
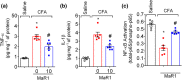
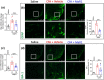
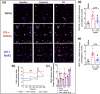
Key results: MaR1 reduced carrageenan- and CFA-induced mechanical and thermal hyperalgesia and neutrophil and macrophage recruitment proximal to CGRP+ fibres in the paw skin. Moreover, MaR1 reduced NF-κB activation, IL-1β and TNF-α production, and spinal cord glial cells activation. In the DRG, MaR1 reduced CFA-induced Nav1.8 and Trpv1 mRNA expression and calcium influx and capsaicin-induced release of CGRP by DRG neurons.
Conclusions and implications: MaR1 reduced DRG neurons activation and CGRP release explaining, at least in part, its analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects. The enduring analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects and also post-treatment activity of MaR1 suggest that specialised pro-resolving lipid mediators have potential as a new class of drugs for the treatment of inflammatory pain.
© 2019 The British Pharmacological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Maresin 2 is an analgesic specialized pro-resolution lipid mediator in mice by inhibiting neutrophil and monocyte recruitment, nociceptor neuron TRPV1 and TRPA1 activation, and CGRP release.Neuropharmacology. 2022 Sep 15;216:109189. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2022.109189. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Neuropharmacology. 2022. PMID: 35820471
-
4-Methylesculetin attenuates inflammatory pain via inhibition of Sp1-TRPV1 and inflammation related signaling pathways.Int Immunopharmacol. 2025 Apr 16;152:114379. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2025.114379. Epub 2025 Mar 6. Int Immunopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40054325
-
Specialized pro-resolving mediator Maresin 1 attenuates pain in a mouse model of osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2025 Mar;33(3):341-350. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2024.10.018. Epub 2024 Nov 29. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2025. PMID: 39617202
-
Novel strategies for the treatment of inflammatory hyperalgesia.Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010 May;66(5):429-44. doi: 10.1007/s00228-010-0784-7. Epub 2010 Feb 13. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20155257 Review.
-
Maresin1: A multifunctional regulator in inflammatory bone diseases.Int Immunopharmacol. 2023 Jul;120:110308. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110308. Epub 2023 May 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37192551 Review.
Cited by
-
Pain-resolving immune mechanisms in neuropathic pain.Nat Rev Neurol. 2023 Apr;19(4):199-220. doi: 10.1038/s41582-023-00777-3. Epub 2023 Mar 1. Nat Rev Neurol. 2023. PMID: 36859719 Review.
-
Role of Specialized Pro-Resolving Mediators in Neuropathic Pain.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 11;12:717993. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.717993. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34456731 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Harnessing Inflammation Resolution in Arthritis: Current Understanding of Specialized Pro-resolving Lipid Mediators' Contribution to Arthritis Physiopathology and Future Perspectives.Front Physiol. 2021 Sep 1;12:729134. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.729134. eCollection 2021. Front Physiol. 2021. PMID: 34539449 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maresin-1 and Inflammatory Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 25;23(3):1367. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031367. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Maresin-1 ameliorates hypertensive vascular remodeling through its receptor LGR6.MedComm (2020). 2024 Mar 9;5(3):e491. doi: 10.1002/mco2.491. eCollection 2024 Mar. MedComm (2020). 2024. PMID: 38463394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alexander, S. P. , Christopoulos, A. , Davenport, A. P. , Kelly, E. , Marrion, N. V. , Peters, J. A. , … CGTP Collaborators . (2017). The Concise Guide to PHARMACOLOGY 2017/18: G protein‐coupled receptors. British Journal of Pharmacology, 174(Suppl 1), S17–S129. 10.1111/bph.13878 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

