Altered limbic and autonomic processing supports brain-heart axis in Takotsubo syndrome
- PMID: 30831580
- PMCID: PMC6462306
- DOI: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz068
Altered limbic and autonomic processing supports brain-heart axis in Takotsubo syndrome
Abstract
Aims: Takotsubo syndrome (TTS) is characterized by acute left ventricular dysfunction often triggered by emotional or physical stress. Severe activation of the sympathetic nervous system with catecholamine release caused by a dysfunctional limbic system has been proposed as a potential mechanism. We hypothesize that brain regions responsible for autonomic integration and/or limbic processing might be involved in the development of TTS. Here, we investigated alterations in resting state functional connectivity in TTS patients compared with healthy controls.
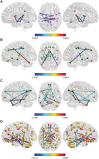
Methods and results: Using brain functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI), resting state functional connectivity has been assessed in 15 subjects with TTS and 39 healthy controls. Network-based statistical analyses were conducted to identify subnetworks with altered resting state functional connectivity. Sympathetic and parasympathetic networks have been constructed in addition to the default mode network and whole-brain network. We found parasympathetic- and sympathetic-associated subnetworks both showing reduced resting state functional connectivity in TTS patients compared with controls. Important brain regions constituting parasympathetic- and sympathetic-associated subnetworks included the amygdala, hippocampus, and insula as well as cingulate, parietal, temporal, and cerebellar regions. Additionally, the default mode network as well as limbic regions in the whole-brain analysis demonstrated reduced resting state functional connectivity in TTS, including the hippocampus, parahippocampal, and medial prefrontal regions.
Conclusion: For the first time, we demonstrate hypoconnectivity of central brain regions associated with autonomic functions and regulation of the limbic system in patients with TTS. These findings suggest that autonomic-limbic integration might play an important role in the pathophysiology and contribute to the understanding of TTS.
Keywords: Sympathetic; Autonomic-limbic integration; Brain–heart connection; Parasympathetic; Resting state fMRI; Takotsubo syndrome.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the European Society of Cardiology.
Figures
Comment in
-
Brain-heart axis in Takotsubo syndrome.Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019 May;16(5):258. doi: 10.1038/s41569-019-0181-6. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2019. PMID: 30874630 No abstract available.
-
Neurocardiology: the brain-heart connection in Takotsubo syndrome.Eur Heart J. 2019 Sep 21;40(36):3062-3063. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz499. Eur Heart J. 2019. PMID: 31302668 No abstract available.
-
Central autonomic network and Takotsubo cardiomyopathy: how left insular cortex interact?Eur Heart J. 2019 Sep 21;40(36):3061. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehz476. Eur Heart J. 2019. PMID: 31302672 No abstract available.
References
-
- Samuels MA. The brain-heart connection. Circulation 2007;116:77–84. - PubMed
-
- Templin C, Ghadri JR, Diekmann J, Napp LC, Bataiosu DR, Jaguszewski M, Cammann VL, Sarcon A, Geyer V, Neumann CA, Seifert B, Hellermann J, Schwyzer M, Eisenhardt K, Jenewein J, Franke J, Katus HA, Burgdorf C, Schunkert H, Moeller C, Thiele H, Bauersachs J, Tschöpe C, Schultheiss H-P, Laney CA, Rajan L, Michels G, Pfister R, Ukena C, Böhm M, Erbel R, Cuneo A, Kuck K-H, Jacobshagen C, Hasenfuss G, Karakas M, Koenig W, Rottbauer W, Said SM, Braun-Dullaeus RC, Cuculi F, Banning A, Fischer TA, Vasankari T, Airaksinen KEJ, Fijalkowski M, Rynkiewicz A, Pawlak M, Opolski G, Dworakowski R, MacCarthy P, Kaiser C, Osswald S, Galiuto L, Crea F, Dichtl W, Franz WM, Empen K, Felix SB, Delmas C, Lairez O, Erne P, Bax JJ, Ford I, Ruschitzka F, Prasad A, Lüscher TF.. Clinical features and outcomes of Takotsubo (stress) cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med 2015;373:929–938. - PubMed
-
- Ghadri JR, Sarcon A, Diekmann J, Bataiosu DR, Cammann VL, Jurisic S, Napp LC, Jaguszewski M, Scherff F, Brugger P, Jäncke L, Seifert B, Bax JJ, Ruschitzka F, Luscher TF, Templin C, InterTAK Co-investigators. Happy heart syndrome: role of positive emotional stress in takotsubo syndrome. Eur Heart J 2016;37:2823–2829. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hiestand T, Hänggi J, Klein C, Topka MS, Jaguszewski M, Ghadri JR, Luscher TF, Jäncke L, Templin C.. Takotsubo syndrome associated with structural brain alterations of the limbic system. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018;71:809–811. - PubMed
-
- Templin C, Napp LC, Ghadri JR.. Takotsubo syndrome: underdiagnosed, underestimated, but understood? J Am Coll Cardiol 2016;67:1937–1940. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

