Efficacy of an Adjuvanted Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike Protein Vaccine in Dromedary Camels and Alpacas
- PMID: 30832356
- PMCID: PMC6466352
- DOI: 10.3390/v11030212
Efficacy of an Adjuvanted Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Spike Protein Vaccine in Dromedary Camels and Alpacas
Abstract
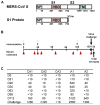
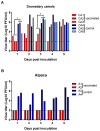
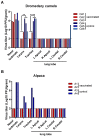
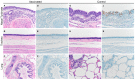
MERS-CoV is present in dromedary camels throughout the Middle East and Africa. Dromedary camels are the primary zoonotic reservoir for human infections. Interruption of the zoonotic transmission chain from camels to humans, therefore, may be an effective strategy to control the ongoing MERS-CoV outbreak. Here we show that vaccination with an adjuvanted MERS-CoV Spike protein subunit vaccine confers complete protection from MERS-CoV disease in alpaca and results in reduced and delayed viral shedding in the upper airways of dromedary camels. Protection in alpaca correlates with high serum neutralizing antibody titers. Lower titers of serum neutralizing antibodies correlate with delayed and significantly reduced shedding in the nasal turbinates of dromedary camels. Together, these data indicate that induction of robust neutralizing humoral immune responses by vaccination of naïve animals reduces shedding that potentially could diminish the risk of zoonotic transmission.
Keywords: MERS-CoV; One Health; camels; vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- WHO Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus (MERS-CoV) [(accessed on 1 December 2018)]; Available online: http://www.who.int/emergencies/mers-cov/en/
-
- Azhar E.I., Hashem A.M., El-Kafrawy S.A., Sohrab S.S., Aburizaiza A.S., Farraj S.A., Hassan A.M., Al-Saeed M.S., Jamjoom G.A., Madani T.A. Detection of the Middle East Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus Genome in an Air Sample Originating from a Camel Barn Owned by an Infected Patient. mBio. 2014;5:e01450-14. doi: 10.1128/mBio.01450-14. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

