Ethanolamine Utilization and Bacterial Microcompartment Formation Are Subject to Carbon Catabolite Repression
- PMID: 30833356
- PMCID: PMC6482927
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00703-18
Ethanolamine Utilization and Bacterial Microcompartment Formation Are Subject to Carbon Catabolite Repression
Abstract
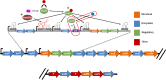
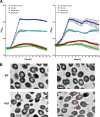
Ethanolamine (EA) is a compound prevalent in the gastrointestinal (GI) tract that can be used as a carbon, nitrogen, and/or energy source. Enterococcus faecalis, a GI commensal and opportunistic pathogen, contains approximately 20
Keywords: bacterial microcompartments; carbon catabolite repression; enterococcus; ethanolamine utilization.
Copyright © 2019 American Society for Microbiology.
Figures





References
-
- White DA. 1973. Phospholipid composition of mammalian tissues, p 441–482. In Ansell GB, Hawthorne JN, Dawson RMC (ed), Form and function of phospholipids. Elsevier, New York, NY.
-
- Bertin Y, Girardeau JP, Chaucheyras-Durand F, Lyan B, Pujos-Guillot E, Harel J, Martin C. 2011. Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli gains a competitive advantage by using ethanolamine as a nitrogen source in the bovine intestinal content. Environ Microbiol 13:365–377. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2010.02334.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

