Renal reabsorption in 3D vascularized proximal tubule models
- PMID: 30833403
- PMCID: PMC6431199
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1815208116
Renal reabsorption in 3D vascularized proximal tubule models
Abstract
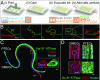
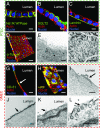
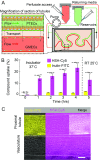
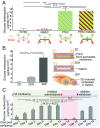
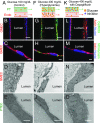
Three-dimensional renal tissues that emulate the cellular composition, geometry, and function of native kidney tissue would enable fundamental studies of filtration and reabsorption. Here, we have created 3D vascularized proximal tubule models composed of adjacent conduits that are lined with confluent epithelium and endothelium, embedded in a permeable ECM, and independently addressed using a closed-loop perfusion system to investigate renal reabsorption. Our 3D kidney tissue allows for coculture of proximal tubule epithelium and vascular endothelium that exhibits active reabsorption via tubular-vascular exchange of solutes akin to native kidney tissue. Using this model, both albumin uptake and glucose reabsorption are quantified as a function of time. Epithelium-endothelium cross-talk is further studied by exposing proximal tubule cells to hyperglycemic conditions and monitoring endothelial cell dysfunction. This diseased state can be rescued by administering a glucose transport inhibitor. Our 3D kidney tissue provides a platform for in vitro studies of kidney function, disease modeling, and pharmacology.
Keywords: bioprinting; kidney tissue; proximal tubule; reabsorption; vasculature.
Copyright © 2019 the Author(s). Published by PNAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: The authors have filed a patent on this work. A.M. is an employee of Roche Pharmaceutical company and J.A.L. is a cofounder of Voxel8, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Eaton D, Pooler J. 2004. Vander’s Renal Physiology, Lange Physiology Series (Lange Medical Books/McGraw-Hill, New York)
-
- Wilmer MJ, et al. Kidney-on-a-chip technology for drug-induced nephrotoxicity screening. Trends Biotechnol. 2016;34:156–170. - PubMed
-
- Jang K-J, et al. Human kidney proximal tubule-on-a-chip for drug transport and nephrotoxicity assessment. Integr Biol. 2013;5:1119–1129. - PubMed
-
- Meyers CM, Seeff LB, Stehman-Breen CO, Hoofnagle JH. Hepatitis C and renal disease: An update. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003;42:631–657. - PubMed
-
- Lazzara MJ, Deen WM. Model of albumin reabsorption in the proximal tubule. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2007;292:F430–F439. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

