Proteus mirabilis Producing the OXA-58 Carbapenemase in Poland
- PMID: 30833423
- PMCID: PMC6496089
- DOI: 10.1128/AAC.00106-19
Proteus mirabilis Producing the OXA-58 Carbapenemase in Poland
Keywords: Enterobacterales; OXA-58; Proteus mirabilis; carbapenemase; class D carbapenemase.
Figures
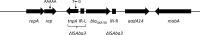
References
-
- Leski TA, Bangura U, Jimmy DH, Ansumana R, Lizewski SE, Li RW, Stenger DA, Taitt CR, Vora GJ. 2013. Identification of blaOXA-51-like, blaOXA-58, blaDIM-1, and blaVIM carbapenemase genes in hospital Enterobacteriaceae isolates from Sierra Leone. J Clin Microbiol 51:2435–2438. doi:10.1128/JCM.00832-13. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

