DNA Damage Does Not Cause BrdU Labeling of Mouse or Human β-Cells
- PMID: 30833468
- PMCID: PMC6477907
- DOI: 10.2337/db18-0761
DNA Damage Does Not Cause BrdU Labeling of Mouse or Human β-Cells
Abstract
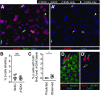
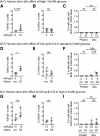
Pancreatic β-cell regeneration, the therapeutic expansion of β-cell number to reverse diabetes, is an important goal. Replication of differentiated insulin-producing cells is the major source of new β-cells in adult mice and juvenile humans. Nucleoside analogs such as BrdU, which are incorporated into DNA during S-phase, have been widely used to quantify β-cell proliferation. However, reports of β-cell nuclei labeling with both BrdU and γ-phosphorylated H2A histone family member X (γH2AX), a DNA damage marker, have raised questions about the fidelity of BrdU to label S-phase, especially during conditions when DNA damage is present. We performed experiments to clarify the causes of BrdU-γH2AX double labeling in mouse and human β-cells. BrdU-γH2AX colabeling is neither an age-related phenomenon nor limited to human β-cells. DNA damage suppressed BrdU labeling and BrdU-γH2AX colabeling. In dispersed islet cells, but not in intact islets or in vivo, pro-proliferative conditions promoted both BrdU and γH2AX labeling, which could indicate DNA damage, DNA replication stress, or cell cycle-related intrinsic H2AX phosphorylation. Strategies to increase β-cell number must not only tackle the difficult challenge of enticing a quiescent cell to enter the cell cycle, but also achieve safe completion of the cell division process.
© 2019 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Id3 upregulates BrdU incorporation associated with a DNA damage response, not replication, in human pancreatic β-cells.Islets. 2011 Nov-Dec;3(6):358-66. doi: 10.4161/isl.3.6.17923. Epub 2011 Nov 1. Islets. 2011. PMID: 21964314 Free PMC article.
-
Histone H2AX phosphorylation induced by selective photolysis of BrdU-labeled DNA with UV light: relation to cell cycle phase.Cytometry A. 2004 Nov;62(1):1-7. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.20086. Cytometry A. 2004. PMID: 15455410
-
Studies on BrdU labeling of hematopoietic cells: stem cells and cell lines.J Cell Physiol. 2003 Nov;197(2):251-60. doi: 10.1002/jcp.10357. J Cell Physiol. 2003. PMID: 14502565
-
BrdU immunohistochemistry for studying adult neurogenesis: paradigms, pitfalls, limitations, and validation.Brain Res Rev. 2007 Jan;53(1):198-214. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2006.08.002. Epub 2006 Oct 3. Brain Res Rev. 2007. PMID: 17020783 Review.
-
[Application of bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) and anti-BrdU monoclonal antibody for the analysis of tumor cell kinetics by flow cytometry].Nihon Rinsho. 1992 Oct;50(10):2333-7. Nihon Rinsho. 1992. PMID: 1280304 Review. Japanese.
Cited by
-
Design, Synthesis, and Antitumor Evaluation of an Opioid Growth Factor Bioconjugate Targeting Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Feb 16;16(2):283. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16020283. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 38399336 Free PMC article.
-
Mitogen Synergy: An Emerging Route to Boosting Human Beta Cell Proliferation.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jan 27;9:734597. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.734597. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35155441 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Induced Proliferation Remains Intact in Aging Mouse β-Cells.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Aug 31;12:734079. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.734079. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34531828 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Heme Oxygenase-1 on c-Kit-Positive Cardiac Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 15;22(24):13448. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413448. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34948245 Free PMC article.
-
Inadequate β-cell mass is essential for the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes.Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020 Mar;8(3):249-256. doi: 10.1016/S2213-8587(20)30022-X. Epub 2020 Jan 29. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020. PMID: 32006519 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dor Y, Brown J, Martinez OI, Melton DA. Adult pancreatic beta-cells are formed by self-duplication rather than stem-cell differentiation. Nature 2004;429:41–46 - PubMed

