Integrated Analysis of Whole Exome Sequencing and Copy Number Evaluation in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 30833663
- PMCID: PMC6399448
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-40102-x
Integrated Analysis of Whole Exome Sequencing and Copy Number Evaluation in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
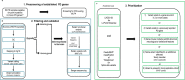
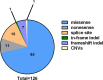
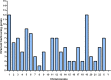
Genetic studies of the familial forms of Parkinson's disease (PD) have identified a number of causative genes with an established role in its pathogenesis. These genes only explain a fraction of the diagnosed cases. The emergence of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) expanded the scope of rare variants identification in novel PD related genes. In this study we describe whole exome sequencing (WES) genetic findings of 60 PD patients with 125 variants validated in 51 of these cases. We used strict criteria for variant categorization that generated a list of variants in 20 genes. These variants included loss of function and missense changes in 18 genes that were never previously linked to PD (NOTCH4, BCOR, ITM2B, HRH4, CELSR1, SNAP91, FAM174A, BSN, SPG7, MAGI2, HEPHL1, EPRS, PUM1, CLSTN1, PLCB3, CLSTN3, DNAJB9 and NEFH) and 2 genes that were previously associated with PD (EIF4G1 and ATP13A2). These genes either play a critical role in neuronal function and/or have mouse models with disease related phenotypes. We highlight NOTCH4 as an interesting candidate in which we identified a deleterious truncating and a splice variant in 2 patients. Our combined molecular approach provides a comprehensive strategy applicable for complex genetic disorders.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- de Rijk MC, et al. Prevalence of Parkinson’s disease in Europe: A collaborative study of population-based cohorts. Neurologic Diseases in the Elderly Research Group. Neurology. 2000;54:S21–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

