Merits and pitfalls of conventional and covalent docking in identifying new hydroxyl aryl aldehyde like compounds as human IRE1 inhibitors
- PMID: 30833722
- PMCID: PMC6399222
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-39939-z
Merits and pitfalls of conventional and covalent docking in identifying new hydroxyl aryl aldehyde like compounds as human IRE1 inhibitors
Abstract
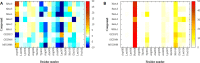
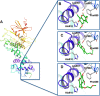
IRE1 is an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) bound transmembrane bifunctional kinase and endoribonuclease protein crucial for the unfolded protein response (UPR) signaling pathway. Upon ER stress, IRE1 homodimerizes, oligomerizes and autophosphorylates resulting in endoribonuclease activity responsible for excision of a 26 nucleotide intron from the X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) mRNA. This unique splicing mechanism results in activation of the XBP1s transcription factor to specifically restore ER stress. Small molecules targeting the reactive lysine residue (Lys907) in IRE1α's RNase domain have been shown to inhibit the cleavage of XBP1 mRNA. Crystal structures of murine IRE1 in complex with covalently bound hydroxyl aryl aldehyde (HAA) inhibitors show that these molecules form hydrophobic interactions with His910 and Phe889, a hydrogen bond with Tyr892 and an indispensable Schiff-base with Lys907. The availability of such data prompted interest in exploring structure-based drug design as a strategy to develop new covalently binding ligands. We extensively evaluated conventional and covalent docking for drug discovery targeting the catalytic site of the RNase domain. The results indicate that neither computational approach is fully successful in the current case, and we highlight herein the potential and limitations of the methods for the design of novel IRE1 RNase binders.
Conflict of interest statement
A.M.G., A.S. and L.A.E. are directors and shareholders of Cell Stress Discoveries, Ltd. A.C. and C.C. declare no potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Walter PDR. The Unfolded Protein Response: From Stress Pathway to Homeostatic Regulation. Science. 2006;34:1081–1087. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

