Structural basis of broad ebolavirus neutralization by a human survivor antibody
- PMID: 30833785
- PMCID: PMC6402988
- DOI: 10.1038/s41594-019-0191-4
Structural basis of broad ebolavirus neutralization by a human survivor antibody
Abstract
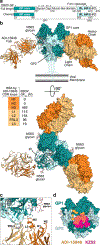
The structural features that govern broad-spectrum activity of broadly neutralizing anti-ebolavirus antibodies (Abs) outside of the internal fusion loop epitope are currently unknown. Here we describe the structure of a broadly neutralizing human monoclonal Ab (mAb), ADI-15946, which was identified in a human survivor of the 2013-2016 outbreak. The crystal structure of ADI-15946 in complex with cleaved Ebola virus glycoprotein (EBOV GPCL) reveals that binding of the mAb structurally mimics the conserved interaction between the EBOV GP core and its glycan cap β17-β18 loop to inhibit infection. Both endosomal proteolysis of EBOV GP and binding of mAb FVM09 displace this loop, thereby increasing exposure of ADI-15946's conserved epitope and enhancing neutralization. Our work also mapped the paratope of ADI-15946, thereby explaining reduced activity against Sudan virus, which enabled rational, structure-guided engineering to enhance binding and neutralization of Sudan virus while retaining the parental activity against EBOV and Bundibugyo virus.
Figures




References
-
- Corti D et al. Protective monotherapy against lethal Ebola virus infection by a potently neutralizing antibody. Science 351, 1339–1342 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Cox E et al. Notes for the record: consultation on monitored emergency use of unregistered and investigational interventions for Ebola virus disease. World Health Organization; (2018). Available at: http://www.who.int/emergencies/ebola/MEURI-Ebola.pdf?ua=1 (Accessed: 17th August 2018)
-
- Sivapalasingam S et al. Safety, pharmacokinetics, and immunogenicity of a co-formulated cocktail of three human monoclonal antibodies targeting Ebola virus glycoprotein in healthy adults: a randomised, first-in-human phase 1 study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 18, 884–893 (2018). - PubMed
Methods-only references:
-
- McPhillips TM et al. Blu-Ice and the distributed control system: software for data acquisition and instrument control at macromolecular crystallography beamlines. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 9, 401–406 (2002). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

