Rat-borne diseases at the horizon. A systematic review on infectious agents carried by rats in Europe 1995-2016
- PMID: 30834071
- PMCID: PMC6394330
- DOI: 10.1080/20008686.2018.1553461
Rat-borne diseases at the horizon. A systematic review on infectious agents carried by rats in Europe 1995-2016
Abstract
To investigate the spectrum of rat-borne pathogens circulating in Europe a systematic review spanning across 55 European countries during the years 1995-2016 was performed. The study surveyed viruses, bacteria, macroparasites and unicellular eukaryotes (protozoa). Fifty-three different infectious agents, all with zoonotic potential, were reported to be carried by commensal rats; 48 by the brown rat (Rattus norvegicus) and 20 by the black rat (R. rattus). There was a tendency for rural areas to harbour more rat-borne microbes than urban areas regarding the brown rat, but the opposite could be observed for the black rat. The study clearly indicated that an improved surveillance on wild rats is needed in Europe, and further indicated the pathogens and geographical areas where the major focus is required. For example, six zoonotic microbes seemed to be clearly more geographically widespread in Europe than others; virulent or resistant E. coli, pathogenic Leptospira spp., Hymenolepis diminuta, H. nana, Capillaria hepatica and Toxoplasma gondii.
Keywords: Capillaria; Europe; Hymenolepis; Leptospira; Rattus; zoonoses.
Figures
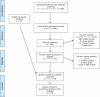

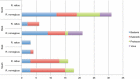
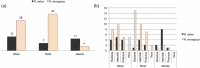
References
-
- Pijnacker R, Goris MG, Te Wierik MJ, et al. Marked increase in leptospirosis infections in humans and dogs in the Netherlands, 2014. Eurosurveillance. 2016;21:23–9. - PubMed
-
- Buckle A.Anticoagulant resistance in the UK and a new guideline for the management of resistant infestations of Norway rats (Rattus norvegicus berk.). Pest Manag Sci. 2013;69:334–341. - PubMed
-
- Meerburg BG, Singleton GR, Kijlstra A. Rodent-borne diseases and their risks for public health. Crit Rev Microbiol. 2009;35:221–270. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
