Oral administration of Ginkgolide B alleviates hypoxia-induced neuronal damage in rat hippocampus by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis
- PMID: 30834078
- PMCID: PMC6396993
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2018.26228.6569
Oral administration of Ginkgolide B alleviates hypoxia-induced neuronal damage in rat hippocampus by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis
Abstract
Objectives: The aim of this study is to explore the potential neuroprotective effects of Ginkgolide B (GB), a main terpene lactone and active component in Ginkgo biloba, in hypoxia-induced neuronal damage, and to further investigate its possible mechanisms.
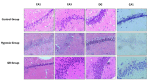
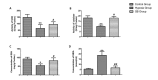
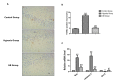
Materials and methods: 54 Sprague-Dawley rats were randomly divided into three groups: the untreated control group (n=18); the hypoxia group (n=18; exposed to 6000 m simulated plateau altitude for six days); and the GB group (n=18; intragastric administration of 12 mg/kg GB three days prior to rapid adaption to 6000 m and on the first two days of hypoxia). After hypoxia exposure for six days, we dissected out the brain hippocampi and performed hematoxylin and eosin staining, Nissl staining, and TUNEL staining. Homogenates of the hippocampi were used to test the oxidative stress indices including malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione (GSH), and catalase. Bax and caspase-3 expression in the hippocampal tissue was measured using qRT-PCR.
Results: Treatment with GB before exposure to hypoxia could protect neural cells and increase the number of Nissl bodies. TUNEL and qRT-PCR results demonstrated that GB treatment could decrease apoptotic cells in different areas of the hippocampus. Antioxidant defense systems such as SOD, GSH, and catalase were decreased (P<0.05), and the concentration of MDA was reduced significantly in the hippocampi of rats of the GB group (P<0.05).
Conclusion: GB could alleviate hypoxia-induced neuronal damage in rat hippocampus by inhibiting oxidative stress and apoptosis.
Keywords: Apoptosis; Ginkgolide B; Hippocampus; Hypoxia; Oxidative stress injury.
Conflict of interest statement
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to subject of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cognitive Protective Mechanism of Crocin Pretreatment in Rat Submitted to Acute High-Altitude Hypoxia Exposure.Biomed Res Int. 2020 Jun 9;2020:3409679. doi: 10.1155/2020/3409679. eCollection 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32596298 Free PMC article.
-
Echinacoside Alleviates Hypoxic-Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rat by Enhancing Antioxidant Capacity and Inhibiting Apoptosis.Neurochem Res. 2019 Jul;44(7):1582-1592. doi: 10.1007/s11064-019-02782-9. Epub 2019 Mar 25. Neurochem Res. 2019. PMID: 30911982
-
Protective effect of ginkgolide B on high altitude cerebral edema of rats.High Alt Med Biol. 2013 Mar;14(1):61-4. doi: 10.1089/ham.2012.1080. High Alt Med Biol. 2013. PMID: 23537262
-
Ginkgolide B‑induced AMPK pathway activation protects astrocytes by regulating endoplasmic reticulum stress, oxidative stress and energy metabolism induced by Aβ1‑42.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jun;23(6):457. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12096. Epub 2021 Apr 21. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 33880582 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological studies supporting the therapeutic use of Ginkgo biloba extract for Alzheimer's disease.Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003 Jun;36 Suppl 1:S8-14. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-40454. Pharmacopsychiatry. 2003. PMID: 13130383 Review.
Cited by
-
Ginkgolide B‑mediated therapeutic effects on perioperative neurocognitive dysfunction are associated with the inhibition of iNOS‑mediated production of NO.Mol Med Rep. 2021 Jul;24(1):537. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12176. Epub 2021 Jun 3. Mol Med Rep. 2021. PMID: 34080648 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of Ginkgo biloba for patients with early diabetic nephropathy: A protocol for systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Aug 28;99(35):e21959. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000021959. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32871945 Free PMC article.
-
Ginkgo Biloba and Long COVID: In Vivo and In Vitro Models for the Evaluation of Nanotherapeutic Efficacy.Pharmaceutics. 2023 May 22;15(5):1562. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15051562. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37242804 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginkgolide B regulates apoptosis, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial dysfunction in MPP+-induced SK-N-SH cells by targeting HDAC4/JNK pathway.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025 Jul;398(7):8899-8908. doi: 10.1007/s00210-025-03815-7. Epub 2025 Jan 29. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39878815
-
[Effect of inhibiting miR-204 expression on the learning and memory abilities of neonatal rats with intrauterine growth restriction and related mechanism].Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022 Dec 15;24(12):1376-1383. doi: 10.7499/j.issn.1008-8830.2205140. Zhongguo Dang Dai Er Ke Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36544422 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Hackett PH, Roach RC. High-altitude illness. N Engl J Med. 2001;345:107–114. - PubMed
-
- Flück M. Functional, structural and molecular plasticity of mammalian skeletal muscle in response to exercise stimuli. J Exp Biol. 2006;209:2239–2248. - PubMed
-
- Kleszczyński K, Zillikens D, Fischer TW. Melatonin enhances mitochondrial ATP synthesis, reduces reactive oxygen species formation, and mediates translocation of the nuclear erythroid 2-related factor 2 resulting in activation of phase-2 antioxidant enzymes (γ-GCS, HO-1, NQO1) in ultraviolet radiation-treated normal human epidermal keratinocytes (NHEK) J Pineal Res. 2016;61:187–197. - PubMed
-
- Niki E. Assessment of antioxidant capacity in vitro and in vivo. Free Radic Biol Med. 2010;49:503–515. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials