Effect of berberine chloride on caspase-3 dependent apoptosis and antioxidant capacity in the hippocampus of the chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rat model
- PMID: 30834080
- PMCID: PMC6396990
- DOI: 10.22038/ijbms.2018.31225.7534
Effect of berberine chloride on caspase-3 dependent apoptosis and antioxidant capacity in the hippocampus of the chronic cerebral hypoperfusion rat model
Abstract
Objectives: The main goal of the current research was to examine the effects of Berberine (BBR) on apoptotic signaling and hippocampal oxidative stress induced by common carotid artery occlusion.
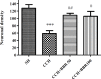
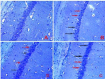
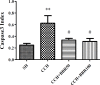
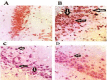
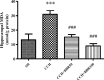
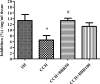
Materials and methods: Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion (CCH) model was created by occluding the two common carotid arteries (two-vessel occlusion [2VO]) permanently. BBR (50 and 100 mg/kg/daily) was intra-gastrically administered to ischemic rats. Neuronal survival was evaluated by Nissl staining. The levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and antioxidant enzymes, including catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase (SOD), along with the activities of caspase 3 were estimated in the hippocampus 2 month after treating the rats with 2VO.
Results: According to findings of the present research, the BBR therapy inhibited the neuro-degeneration of hippocampus. BBR also significantly decreased the amount of MDA and activity of caspase 3 in the hippocampus. Furthermore, the administration of BBR alleviated the lowered activities of SOD and CAT after 2VO surgery.
Conclusion: The antioxidant and antiapoptotic properties of BBR might play important roles in improving functional outcomes and might have significant neuroprotective effects on the CCH damage.
Keywords: Antioxidant enzymes; Apoptosis; Berberine; Chronic cerebral – hypoperfusion; Common carotid artery MDA; Rat.
Conflict of interest statement
The Authors declares that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
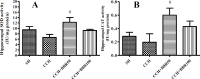
Similar articles
-
Carvacrol suppresses learning and memory dysfunction and hippocampal damages caused by chronic cerebral hypoperfusion.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020 Apr;393(4):581-589. doi: 10.1007/s00210-019-01754-8. Epub 2019 Nov 15. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31729545
-
The Cannabinoid Receptor Agonist WIN55,212-2 Ameliorates Hippocampal Neuronal Damage After Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion Possibly Through Inhibiting Oxidative Stress and ASK1-p38 Signaling.Neurotox Res. 2020 Apr;37(4):847-856. doi: 10.1007/s12640-019-00141-8. Epub 2019 Dec 5. Neurotox Res. 2020. PMID: 31808139
-
Effect of berberine on the hippocampal structure, biochemical factors, memory, and blood-brain barrier in rat model of transient global cerebral ischemia.Phytother Res. 2024 Aug;38(8):4230-4239. doi: 10.1002/ptr.8234. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Phytother Res. 2024. PMID: 38950958
-
HMGB1 Neutralization Attenuates Hippocampal Neuronal Death and Cognitive Impairment in Rats with Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion via Suppressing Inflammatory Responses and Oxidative Stress.Neuroscience. 2018 Jul 15;383:150-159. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.05.010. Epub 2018 May 17. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29777754
-
Permanent, bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in the rat: a model for chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-related neurodegenerative diseases.Brain Res Rev. 2007 Apr;54(1):162-80. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2007.01.003. Epub 2007 Jan 18. Brain Res Rev. 2007. PMID: 17296232 Review.
Cited by
-
Neuroprotective Properties of Berberine: Molecular Mechanisms and Clinical Implications.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Oct 19;12(10):1883. doi: 10.3390/antiox12101883. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37891961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Carvacrol reduces hippocampal cell death and improves learning and memory deficits following lead-induced neurotoxicity via antioxidant activity.Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020 Jul;393(7):1229-1237. doi: 10.1007/s00210-020-01866-6. Epub 2020 Apr 17. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 32303785
-
Berberine Inhibits Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Formation and Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Phenotypic Switching by Regulating the Nrf2 Pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2025 Apr;29(7):e70509. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.70509. J Cell Mol Med. 2025. PMID: 40193135 Free PMC article.
-
Dataset on biochemical markers and histological alterations in rat kidney intoxicated with cadmium chloride and treated with antioxidant.Data Brief. 2022 Jun 17;43:108394. doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2022.108394. eCollection 2022 Aug. Data Brief. 2022. PMID: 35789907 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin attenuates cerebral hypoperfusion-induced hippocampal damage and memory deficits in rats by suppressing TRPM7 channels.Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022 Apr;29(4):2958-2968. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2022.01.018. Epub 2022 Jan 18. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35531206 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harukuni I, Bhardwaj A. Mechanisms of brain injury after global cerebral ischemia. Neurologic clinics. 2006;24:1–21. - PubMed
-
- Gheibi S, Aboutaleb N, Khaksari M, Kalalian-Moghaddam H, Vakili A, Asadi Y, et al. Hydrogen sulfide protects the brain against ischemic reperfusion injury in a transient model of focal cerebral ischemia. J Mol Neurosci. 2014;54:264–270. - PubMed
-
- Farkas E, Luiten PG, Bari F. Permanent, bilateral common carotid artery occlusion in the rat: a model for chronic cerebral hypoperfusion-related neurodegenerative diseases. Brain Res Rev. 2007;54:162–180. - PubMed
-
- Lee JS, Im DS, An Y-S, Hong JM, Gwag BJ, Joo IS. Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: an additional contributing factor of cognitive impairment. Neurosci Lett. 2011;489:84–88. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
