Different Neural Correlates of Automatic Emotion Regulation at Implicit and Explicit Perceptual Level: A Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
- PMID: 30834098
- PMCID: PMC6393835
- DOI: 10.1177/2041669519831028
Different Neural Correlates of Automatic Emotion Regulation at Implicit and Explicit Perceptual Level: A Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging Study
Abstract
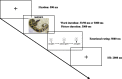
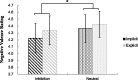
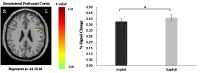
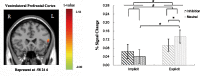
Automatic emotion regulation (AER) is an important type of emotion regulation in our daily life. Most of the previous studies concerning AER are done in the conscious level. Little is known about the AER under the subliminal level. The present study was to investigate the AER at the different perceptual levels (i.e., explicitly and implicitly) simultaneously, and the associated neural differences using functional magnetic resonance imaging. Priming paradigm was adopted in which the inhibition or neutral words were used as primes and the negative picutres were used as targets. In the experiment, the duration time of priming words was manipulated at 33 or 50 ms in the implicit level and 3000 ms in the explicit level. The participants were required to make emotional valence rating of the negative pictures while undergoing functional magnetic resonance imaging scanning. The results showed that the participants experienced less negative emotion in inhibition words priming condition contrary to neutral words priming condition. Significant differences were also found in the left ventrolateral prefrontal cortex and left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex at the implicit and explicit AER. The findings of this study demonstrate that inhibition words can automatically and effectively reduce an individual's negative emotion experience, and left ventrolateral prefrontal cortex and left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex have been both implicated in self-control during AER.
Keywords: automatic emotion regulation; explicit; functional magnetic resonance imaging; implicit; perceptual level.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Suppress to feel and remember less: Neural correlates of explicit and implicit emotional suppression on perception and memory.Neuropsychologia. 2020 Aug;145:106683. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2018.02.010. Epub 2018 Feb 9. Neuropsychologia. 2020. PMID: 29432767
-
Automatic adaptive emotion regulation is associated with lower emotion-related activation in the frontoparietal cortex and other cortical regions with multi-componential organization.Front Behav Neurosci. 2023 Mar 6;17:1059158. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1059158. eCollection 2023. Front Behav Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 36950064 Free PMC article.
-
Facial expression primes and implicit regulation of negative emotion.Neuroreport. 2015 Jun 17;26(9):548-53. doi: 10.1097/WNR.0000000000000383. Neuroreport. 2015. PMID: 26011391
-
Separate neural networks of implicit emotional processing between pictures and words: A coordinate-based meta-analysis of brain imaging studies.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021 Dec;131:331-344. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2021.09.041. Epub 2021 Sep 22. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2021. PMID: 34562542 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Explicit and implicit emotion regulation: a dual-process framework.Cogn Emot. 2011 Apr;25(3):400-12. doi: 10.1080/02699931.2010.544160. Cogn Emot. 2011. PMID: 21432682 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aarts H., Dijksterhuis A. (2000) Habits as knowledge structures: Automaticity in goal directed behavior. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology 78: 53–63. - PubMed
-
- Adams G., Markus H. R. (2004) Toward a conception of culture suitable for a social psychology of culture. In: Schaller M., Crandall C. S. (eds) The psychological foundations of culture, Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates, pp. 335–360.
-
- Aron A. R., Robbins T. W., Poldrack R. A. (2014) Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex: One decade on. Trends in Cognitive Sciences 18: 177–185. - PubMed
-
- Bai L., Ma H., Huang Y. X., Luo Y. J. (2005) The development of native Chinese affective picture system—A pretest in 46 college students. Chinese Mental Health Journal 19: 719–722.

