Understanding the impact of neurologic complications in patients with cirrhosis
- PMID: 30834114
- PMCID: PMC6396044
- DOI: 10.1177/2050312119832090
Understanding the impact of neurologic complications in patients with cirrhosis
Abstract
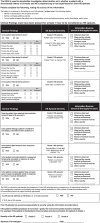
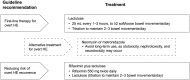
Patients with cirrhosis may experience neurologic complications, including hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatic encephalopathy may be classified as covert (mild symptoms (e.g. lack of awareness)) or overt (moderate to severe symptoms (e.g. confusion or coma)), and symptoms may overlap with other neurologic conditions (e.g. epilepsy, stroke). Managing hepatic encephalopathy includes identifying and treating precipitating factors (e.g. dehydration). First-line treatment for patients with overt hepatic encephalopathy is typically lactulose; to reduce the risk of overt hepatic encephalopathy recurrence, lactulose plus the nonsystemic antibiotic rifaximin is recommended. Rifaximin reduced the risk of breakthrough overt hepatic encephalopathy by 58% versus placebo over 6 months (p < 0.001; 91% of patients in each group were on concomitant lactulose). However, neither pharmacologic hepatic encephalopathy treatment nor liver transplantation may completely reverse neurologic impairment in patients with hepatic encephalopathy. Additional neurologic considerations for patients with cirrhosis include preventing falls, as well as managing sleep-related issues, hyponatremia, and cerebral edema. Thus, monitoring neurologic impairment is an important component in the management of patients with cirrhosis.
Keywords: Hepatic encephalopathy; cognitive impairment; lactulose; rifaximin.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interests: The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Complications of Cirrhosis in Primary Care: Recognition and Management of Hepatic Encephalopathy.Am J Med Sci. 2018 Sep;356(3):296-303. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2018.06.008. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Am J Med Sci. 2018. PMID: 30286824 Review.
-
Overt Hepatic Encephalopathy: Current Pharmacologic Treatments and Improving Clinical Outcomes.Am J Med. 2021 Nov;134(11):1330-1338. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2021.06.007. Epub 2021 Jul 7. Am J Med. 2021. PMID: 34242619 Review.
-
Update on management of patients with overt hepatic encephalopathy.Hosp Pract (1995). 2013 Aug;41(3):48-59. doi: 10.3810/hp.2013.08.1068. Hosp Pract (1995). 2013. PMID: 23948621 Review.
-
Efficacy of rifaximin versus lactulose for reducing the recurrence of overt hepatic encephalopathy and hopitalizations in cirrhosis.Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2012 Oct-Dec;116(4):1021-7. Rev Med Chir Soc Med Nat Iasi. 2012. PMID: 23700882
-
Rifaximin treatment for reduction of risk of overt hepatic encephalopathy recurrence.Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2011 May;4(3):199-206. doi: 10.1177/1756283X11401774. Therap Adv Gastroenterol. 2011. PMID: 21694804 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Minimal hepatic encephalopathy is associated to alterations in eye movements.Sci Rep. 2022 Oct 7;12(1):16837. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-21230-3. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 36207472 Free PMC article.
-
Status epilepticus as an initial manifestation of hepatic encephalopathy: A case report.World J Clin Cases. 2020 Dec 26;8(24):6480-6486. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v8.i24.6480. World J Clin Cases. 2020. PMID: 33392334 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic alterations in the right anterior insula among patients with cirrhosis without overt hepatic encephalopathy: a magnetic resonance spectroscopy study.Front Neurol. 2024 Jan 11;14:1291478. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2023.1291478. eCollection 2023. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38283679 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Scaglione S, Kliethermes S, Cao G, et al. The epidemiology of cirrhosis in the United States: a population-based study. J Clin Gastroenterol 2015; 49(8): 690–696. - PubMed
-
- D’Amico G, Pasta L, Morabito A, et al. Competing risks and prognostic stages of cirrhosis: a 25-year inception cohort study of 494 patients. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2014; 39(10): 1180–1193. - PubMed
-
- D’Amico G, Garcia-Tsao G, Pagliaro L. Natural history and prognostic indicators of survival in cirrhosis: a systematic review of 118 studies. J Hepatol 2006; 44(1): 217–231. - PubMed
-
- Conn HO, Leevy CM, Vlahcevic ZR, et al. Comparison of lactulose and neomycin in the treatment of chronic portal-systemic encephalopathy. A double blind controlled trial. Gastroenterology 1977; 72(4 Pt. 1): 573–583. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources