Hepatocellular carcinoma after direct-acting antiviral drug treatment in patients with hepatitis C virus
- PMID: 30834341
- PMCID: PMC6386743
- DOI: 10.1002/jgh3.12105
Hepatocellular carcinoma after direct-acting antiviral drug treatment in patients with hepatitis C virus
Abstract
Background and aim: Given the use of direct-acting antivirals (DAAs) to treat hepatitis C virus (HCV), their effects on hepatocarcinogenesis should be determined.
Methods: This study enrolled 349 patients with HCV who underwent DAA treatment at our hospital between 2014 and 2018. Their median age was 65 years, and 184 were male; 301 cases were of HCV serotype 1, and 48 were of serotype 2. The DAA treatment was daclatasvir/asunaprevir in 107 cases, sofosbuvir (SOF)/ledipasvir in 147 cases, ritonavir-boosted ombitasvir/paritaprevir in 28 cases, elbasvir/grazoprevir in 19 cases, and SOF/ribavirin in 48 cases. The patients' histories included hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in 45 cases, liver transplant (LT) in 10 cases, and kidney transplant (KT) in 17 cases.
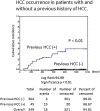
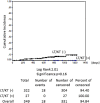
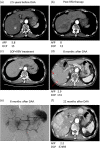
Results: Sustained virological responses occurred in 335 cases (96%). DAA treatment was initiated a median of 16.3 months after HCC treatment. After DAA treatment, 15 cases (33%) had recurrence of HCC after a median of 11.6 months, and 3 cases (1%) developed de novo HCC. Six LT patients and one KT patient had HCC; however, no HCC was observed after DAA. The incidence of HCC was significantly higher in patients with multiple HCC treatments in the Cox hazard model (hazard ratio 1.664, 95% confidence interval 1.134-2.441, P < 0.01). Surgical resection or LT reduced the risk of HCC.
Conclusions: DAA did not increase the rate of HCC, even in immunosuppressed patients. However, careful follow-up for HCC recurrence is required in previously treated cases.
Keywords: direct‐acting antivirals; hepatocarcinogenesis; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Figures

References
-
- Kudo M, Izumi N, Ichida T et al Report of the 19th follow‐up survey of primary liver cancer in Japan. Hepatol. Res. 2016; 46: 372–90. - PubMed
-
- Bartosch B, Thimme R, Blum HE, Zoulim F. Hepatitis C virus‐induced hepatocarcinogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2009; 51: 810–20. - PubMed
-
- Ramzan M, Sturm N, Decaens T et al Liver‐infiltrating CD8(+) lymphocytes as prognostic factor for tumour recurrence in hepatitis C virus‐related hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Int. 2016; 36: 434–44. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

