Effectiveness and Safety of Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant and Warfarin in Cirrhotic Patients With Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
- PMID: 30834802
- PMCID: PMC6474939
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.118.011112
Effectiveness and Safety of Non-Vitamin K Antagonist Oral Anticoagulant and Warfarin in Cirrhotic Patients With Nonvalvular Atrial Fibrillation
Abstract
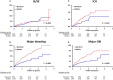
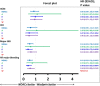
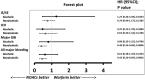
Background Liver cirrhotic patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation have been excluded from randomized clinical studies regarding oral anticoagulants for stroke prevention. Whether non-vitamin K antagonist oral anticoagulants ( NOAC s) are superior to warfarin for these patients remains unclear. Methods and Results This nationwide retrospective cohort study, with data collected from the Taiwan National Health Insurance Research Database, enrolled 2428 liver cirrhotic patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation taking apixaban (n=171), dabigatran (n=535), rivaroxaban (n=732), or warfarin (n=990) from June 1, 2012, to December 31, 2016. We used propensity score-based stabilized weights to balance covariates across study groups. Patients were followed until the occurrence of an event or the end date of study. The NOAC group (n=1438) showed risk of ischemic stroke/systemic embolism and intracranial hemorrhage comparable to that of the warfarin group (n=990) after adjustment. The NOAC group showed significantly lower risk of gastrointestinal bleeding (hazard ratio: 0.51 [95% CI, 0.32-0.79]; P=0.0030) and all major bleeding (hazard ratio: 0.51 [95% CI, 0.32-0.74]; P=0.0003) compared with warfarin group. Overall, 90% (n=1290) of patients were taking a low-dose NOAC (apixaban 2.5 mg twice daily, rivaroxaban 10-15 mg daily, or dabigatran 110 mg twice daily). The subgroup analysis indicated that both dabigatran and rivaroxaban showed lower risk of all major bleeding than warfarin. The advantage of lower gastrointestinal and all major bleeding with NOACs over warfarin is contributed by those subgroups with either nonalcoholic or nonadvanced liver cirrhosis. Conclusions NOACs have a risk of thromboembolism comparable to that of warfarin and a lower risk of major bleeding among liver cirrhotic Asian patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. Consequently, thromboprophylaxis with low-dose NOAC s may be considered for such patients.
Keywords: atrial fibrillation; direct thrombin inhibitor; factor Xa inhibitor; hemorrhage; ischemic stroke; liver cirrhosis; mortality; warfarin.
Figures
Comment in
-
Anticoagulation for Atrial Fibrillation in Cirrhosis of the Liver: Are Low-Dose Non-Vitamin K Oral Anticoagulants a Reasonable Alternative to Warfarin?J Am Heart Assoc. 2019 Mar 5;8(5):e012102. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.012102. J Am Heart Assoc. 2019. PMID: 30834801 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tripodi A, Primignani M, Chantarangkul V, Dell'Era A, Clerici M, de Franchis R, Colombo M, Mannucci PM. An imbalance of pro‐ vs anti‐coagulation factors in plasma from patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2009;137:2105–2111. - PubMed
-
- Northup PG. Hypercoagulation in liver disease. Clin Liver Dis. 2009;13:109–116. - PubMed
-
- Tripodi A, Mannucci PM. The coagulopathy of chronic liver disease. N Engl J Med. 2011;365:147–156. - PubMed
-
- Lin HJ, Wolf PA, Kelly‐Hayes M, Beiser AS, Kase CS, Benjamin EJ, D'Agostino RB. Stroke severity in atrial fibrillation. The Framingham Study. Stroke. 1996;27:1760–1764. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

