Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4-anlinoquinazoline derivatives as EGFR inhibitors with the potential to inhibit the gefitinib-resistant nonsmall cell lung cancers
- PMID: 30835140
- PMCID: PMC6282443
- DOI: 10.1080/14756366.2018.1518957
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel 4-anlinoquinazoline derivatives as EGFR inhibitors with the potential to inhibit the gefitinib-resistant nonsmall cell lung cancers
Abstract
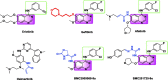
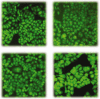
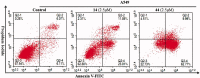
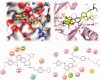
A series of quinazoline derivatives with benzylidene hydrazine carboxamide were designed and synthesised as EGFR inhibitors. Most compounds exhibited exceptional anti-proliferative activity against A549, HepG2, MCF-7 and H1975 cells. Furthermore, six compounds demonstrated excellent inhibition activity against EGFRWT with the IC50 value both less than 2 nM. Among the six compounds, 44 exhibited the strongest activity (0.4 nM) and potently inhibited EGFRL858R/T790M (0.1 μM). Excitingly, the most potent compound 14 showed excellent enzyme inhibitory activity with 6.3 nM and 8.4 nM for both EGFRWT and EGFRT790M/L858R. The result of AO single staining and Annexin V/PI staining showed that the compound 14 and 44 could induce remarkable apoptosis of A549 cells. The compound 14 arrested the cell cycle at the S phase and compound 44 arrested the cell cycle at the G0 phase in A549 cells. These preliminary results demonstrate that compound 14 and 44 may be promising lead compound-targeting EGFR.
Keywords: EGFR; NSCLC; Quinazoline derivatives; benzylidene hydrazine; inhibitors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
New acrylamide-substituted quinazoline derivatives with enhanced potency for the treatment of EGFR T790M-mutant non-small-cell lung cancers.Bioorg Chem. 2018 Apr;77:593-599. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2018.01.035. Epub 2018 Feb 15. Bioorg Chem. 2018. PMID: 29482151
-
Novel, selective acrylamide linked quinazolines for the treatment of double mutant EGFR-L858R/T790M Non-Small-Cell lung cancer (NSCLC).Bioorg Chem. 2021 Oct;115:105234. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2021.105234. Epub 2021 Aug 8. Bioorg Chem. 2021. PMID: 34399322
-
Development of a series of novel 4-anlinoquinazoline derivatives possessing quinazoline skeleton: Design, synthesis, EGFR kinase inhibitory efficacy, and evaluation of anticancer activities in vitro.Eur J Med Chem. 2017 Sep 29;138:669-688. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2017.07.005. Epub 2017 Jul 4. Eur J Med Chem. 2017. PMID: 28711702
-
2-Anilinopyrimidine derivatives: Design, synthesis, in vitro anti-proliferative activity, EGFR and ARO inhibitory activity, cell cycle analysis and molecular docking study.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Jun;99:103798. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.103798. Epub 2020 Mar 29. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 32247112 Review.
-
Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of 2-amino-4-(1,2,4-triazol)pyridine derivatives as potent EGFR inhibitors to overcome TKI-resistance.Eur J Med Chem. 2020 Feb 1;187:111966. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2019.111966. Epub 2019 Dec 14. Eur J Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 31869655 Review.
Cited by
-
Structure-Activity Relationship Studies Based on Quinazoline Derivatives as EGFR Kinase Inhibitors (2017-Present).Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 3;16(4):534. doi: 10.3390/ph16040534. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111291 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design, synthesis and antitumor activity of 5-trifluoromethylpyrimidine derivatives as EGFR inhibitors.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022 Dec;37(1):2742-2754. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2022.2128797. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2022. PMID: 36176072 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Song Z, Ge Y, Wang C, et al. . Challenges and perspectives on the development of small-molecule EGFR inhibitors against T790M-mediated resistance in non-small-cell lung cancer. J. Med. Chem 2016;59:6580–94. - PubMed
-
- Zhang H-Q, Gong F-H, Ye J-Q, et al. . Design and discovery of 4-anilinoquinazoline-urea derivatives as dual TK inhibitors of EGFR and VEGFR-2. Eur J Med Chem 2017;125:245–54. - PubMed
-
- Han J, Henriksen S, Nørsett KG, et al. . Balancing potency, metabolic stability and permeability in pyrrolopyrimidine-based EGFR inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 2016;124:583–607. - PubMed
-
- Amin KM, Barsoum FF, Awadallah FM, et al. . Identification of new potent phthalazine derivatives with VEGFR-2 and EGFR kinase inhibitory activity. Eur J Med Chem 2016;123:191–201. - PubMed
-
- Chen L, Fu W, Feng C, et al. . Structure-based design and synthesis of 2,4-diaminopyrimidines as EGFR L858R/T790M selective inhibitors for NSCLC. Eur J Med Chem 2017;140:510–27. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
