Source or Sink: Examining the Role of Biofilms in Transmission of Mycobacterium spp. in Laboratory Zebrafish
- PMID: 30835168
- PMCID: PMC6459265
- DOI: 10.1089/zeb.2018.1689
Source or Sink: Examining the Role of Biofilms in Transmission of Mycobacterium spp. in Laboratory Zebrafish
Abstract
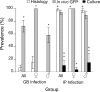
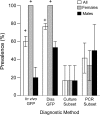
Zebrafish health is a primary research concern because diseases can have unintended impacts on experimental endpoints. Ideally, research would be conducted using disease-free fish or fish with known disease status. Mycobacteriosis is a common bacterial disease in wild and captive fishes, including zebrafish. Despite its prevalence, the dynamics of transmission and potential sources of mycobacterial infections in zebrafish are only partially understood. One suspected natural infection source is surface biofilms on tanks and other system components. This study investigates the role that tank biofilms play in mycobacteriosis in laboratory zebrafish by evaluating the establishment of biofilms from bacteria shed from fish, and conversely, the acquisition of infections in fish from surface biofilms. We found that zebrafish infected with Mycobacterium chelonae shed bacteria through feces, and bacteria are transmitted to tank biofilms from one to 16 weeks postinfection. We also found that zebrafish acquire M. chelonae infections as soon as 2 weeks when introduced to tanks with established M. chelonae biofilms. The results from this study highlight the role that tank biofilms play as both a reservoir and source of mycobacterial infections in zebrafish. Results support the inclusion of biofilm surveillance and prevention as part of a disease control program in zebrafish research facilities.
Keywords: spp.; biofilm; husbandry; zebrafish.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing financial interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Paramecium caudatum enhances transmission and infectivity of Mycobacterium marinum and M. chelonae in zebrafish Danio rerio.Dis Aquat Organ. 2013 Nov 6;106(3):229-39. doi: 10.3354/dao02649. Dis Aquat Organ. 2013. PMID: 24192000 Free PMC article.
-
Husbandry stress exacerbates mycobacterial infections in adult zebrafish, Danio rerio (Hamilton).J Fish Dis. 2009 Nov;32(11):931-41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2009.01074.x. Epub 2009 Jun 13. J Fish Dis. 2009. PMID: 19531062 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogenesis of Mycobacterium spp. in zebrafish (Danio rerio) from research facilities.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2007 Feb;145(1):55-60. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2006.06.004. Epub 2006 Jun 21. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 16904945
-
Mycobacteriosis in fishes: a review.Vet J. 2009 Apr;180(1):33-47. doi: 10.1016/j.tvjl.2008.05.012. Epub 2008 Jul 11. Vet J. 2009. PMID: 18620877 Review.
-
A review of mycobacteriosis in marine fish.J Fish Dis. 2009 Feb;32(2):119-30. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2761.2008.01016.x. J Fish Dis. 2009. PMID: 19261041 Review.
Cited by
-
Transmission of Mycobacterium chelonae and Mycobacterium marinum in laboratory zebrafish through live feeds.J Fish Dis. 2019 Oct;42(10):1425-1431. doi: 10.1111/jfd.13071. Epub 2019 Aug 16. J Fish Dis. 2019. PMID: 31418901 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in susceptibility to Mycobacterium chelonae in zebrafish (Danio rerio) lines commonly used in scientific research.J Fish Dis. 2022 Mar;45(3):435-443. doi: 10.1111/jfd.13572. Epub 2021 Dec 14. J Fish Dis. 2022. PMID: 34905233 Free PMC article.
-
The Influence of Behavioral, Social, and Environmental Factors on Reproducibility and Replicability in Aquatic Animal Models.ILAR J. 2020 Oct 19;60(2):270-288. doi: 10.1093/ilar/ilz019. ILAR J. 2020. PMID: 32400880 Free PMC article.
-
FELASA-AALAS Recommendations for Monitoring and Reporting of Laboratory Fish Diseases and Health Status, with an Emphasis on Zebrafish (Danio Rerio).Comp Med. 2022 Jun 1;72(3):127-148. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-CM-22-000034. Epub 2022 May 5. Comp Med. 2022. PMID: 35513000 Free PMC article.
-
The Effects of Water Volume and Bacterial Concentration on the Water Filtration Assay Used in Zebrafish Health Surveillance.J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2021 Nov 1;60(6):655-660. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-21-000004. Epub 2021 Sep 1. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2021. PMID: 34470695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gaind N. This week in science: trendwatch. Nature 2016;536:131
-
- Kent ML, et al. : Diseases of Zebrafish in Research Facilities. US Environmental Protection Agency, Gulf Breeze, Florida, 2012;2016
-
- Summary of Submissions to the ZIRC Diagnostic Service [ZIRC Public Wiki]. Available at: https://zebrafish.org/wiki/health/submission/report (Accessed 18December, 2018)
-
- Astrofsky KM, Schrenzel MD, Bullis RA, Smolowitz RM, Fox JG. Diagnosis and management of atypical Mycobacterium spp. infections in established laboratory zebrafish (Brachydanio rerio) facilities. Comp Med 2000;50:666–672 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

